INTRODUCTION:
Dl-Methionine is the critical amino-acid for poultry. Supplementation of DL-methionine in poultry ration is well established to improve growth and performance in broilers. (Swick et.al, 1990). Methionine must be supplemented in the diet of chi9cken as the poultry birds are unable to synthesize it in the amounts necessary to sustain life and growth. Methionine is required at higher level than normal level to comply with the increased tissue demands when bird is predisposed to fast growth along with high production performance. The growth rate of birds is often inferior when regardless of amino acid balance, the ratio of crude protein with synthetic amino acid is much less than 16:1 (Lesson & Summers, 2001). Methionine may act as a lipotropic agent through its role as a methyl donor and involvement in choline, betaine, folic acid and vitamin B12 metabolism (March and Bieley, 1956; Chen et.al; 1993). Methionine serves as an integral portion of body protein is a precursor for cysteine and an important source of dietry sulphur. The increase in demand for cheap meat has given rise to the use of synthetic compounds in feed. Recently the safety of such practices has been questioned and their use is becoming restricted to many regions of the world. The DL-methionine supplementation in growing chicken feeds is a common practice especially in cereal and vegetable protein based ration (Swick et al;1990). The synthetic methionine is metabolized into highly toxic comnpounds such as methyl thiopropionate (Baker, 1991) thereby adversely altering the performance of poultry birds. The synthetic methionine is listed among the prohibited synthetic substances (Anon, 1999).
Soaring prices and availability of DL-methionine have forced the researchers to an alternative to replace DL-methionine with an economical alternative in poultry diet. Keeping this in view an attempt is made to overcome the present crises and to validate the claims made on the phytogenic formulation.
The study is designed with an aim to evaluate comparative efficacy of synthetic DL-methionine with Nutri-methionine, a herbal aminoacid developed by M/s Nutricare Life Sciences Shaharanpur, U.P on the performance of broiler chicken.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
One hundred and thirty five day old Vencobb Broiler Chicks were divided into three groups with one control and two treatments having 45 chicks in each group with three replicates of 15 chicks each reared on deep-litter system for a period of 42 days. The research was carried out in the Division of Livestock production & Management, SKUAST of Kashmir.
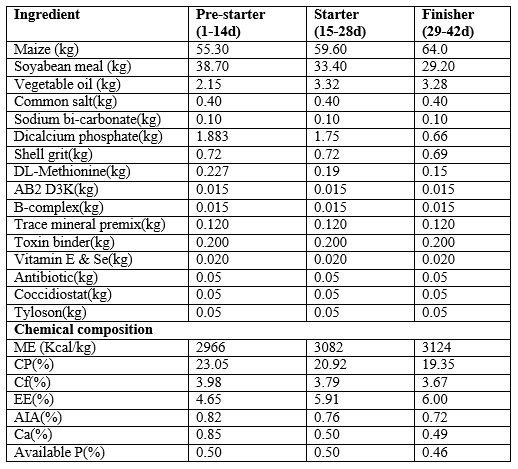
Three types of corn-soyabean meal based diets were offered to the birds i.e, pre-starter (for first 14 days), starter (from 15th to 28th day) and finisher diet (from 29th to 40th day) (Table 1). All the diets were formulated according to BIS (1992). Group I of birds were fed the basal diet without any supplemental Methionine.
Group II of birds were fed the basal diet supplemented with synthetic DL-Methionine @ 100gm per quintal.
Group III of birds were fed the basal diet supplemented with Nutri-Methionine @ 100gm per quintal feed in the diet III.
All the groups were maintained under similar conditions of brooding, feeding and management. Feed was offered ad.libitum throught the experimental period as mash. Weekly body weight and feed consumption were recorded and feed conversion ratio (unit feed intake/unit body weight gain) was calculated. The mortality of birds was recorded as and when it occurred at the end of experimental period blood was collected from two birds from each replicate group (6 birds per replicate) for blood biochemical analysis using commercially available diagnostic kits of span diagnostics. Similarly two birds from each replicate group (6 birds per treatment) were selected randomly and sacrificed as per standard methods for determining the dressing percentage and carcass yield.
The data obtained were subjected to statistical analysis by the soft ware SPSS 10 (SPSS, 1997). Levels of significance were calculated as per the standard methods described by Duncan (1995).
At the end of experimental period blood was collected from two birds from each replicate group (6 birds per replicate) for blood biochemical analysis using commercially available diagnostic kits of span diagnostics. Similarly at the end of the experiment two birds from each replicate group (6 birds per treatment were taken randomly for determining the dressing percentage & carcass yield. The data obtained were subjected to statistical analysis by the software SPSS 10 (SPSS, 1997). Levels of significance were calculated as per the standard method described by Duncan (1995) when ever any effect was found significant.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
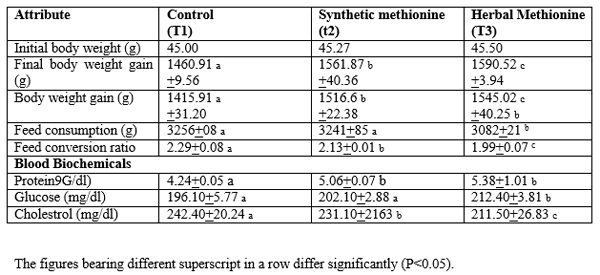
The results of the comparative effect of feeding diets supplemented with synthetic and herbal Methionine on the performance of Broiler chicken is presented in the table 2. The body weight of birds fed herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine) was significantly (P< 0.05) highest when compared with the group of birds fed diets supplemented with synthetic Methionine and negative control diets (without Methionine).
These results are in accordance with the findings of Kiran Kumari et al (2001) and Kadam et al: (2009) Kalbande et al(2009), Naryanswamy and Bhagwat (2010) who reported that, the live body weight gain of birds at 21 days increased significantly as the level of semi-synthetic Methionine was increased in the diet of broiler chicken. Similarly Naranswamy and Bhagwat (2010) reported that the chicks fed herbal Methionine showed a significant (P<0.05) gain in body weight when compared with control group.
Cumulative fed intake was comparable between the group of birds fed diets supplemented with synthetic Methionine when compared with the group of diets fed control diet. However, the feed intake was significantly (P<0.05) lower in the group of birds fed diets supplemented with herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine). These results corroborate with the earlier reports of Chattopadhyay et al(2006) who noted higher feed intake in the control birds than birds supplemented with Methionine (DL-or herbal). However, Kalbande et al (2009) observed no significant effect of herbal or DL-Methionine supplementation on feed consumption of birds.
The feed conversion ratio was improved linearly (P<0.05) among the different treatment groups and the group of birds fed diets supplemented with herbal Methionine (Nutri0methionine) showed the best feed conversion ratio. Similar results have been reported by earlier reporters (Chattopadhyay, 2003; Kiran et al; 2012). It was observed that neither DL-Methionine nor herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine) supplementation had no effect on broiler mortality. The effect of supplementation of herbal Methionine (nutri-Methionine and synthetic Methionine revealed no significant (P<0.05) variation in the defeathered and eviscerated weight amongst the different treatment groups while the dressed weight was numerically higher in the group of birds fed diets supplemented with herbal methionine (Nutri-Methionine). Similar results were earlier recorded by Chattopadhayay, 2003 and Kiran et al; 2012) in the broiler chicken fed, herbal and synthetic aminoacids.
Broiler chicken fed diets supplemented with herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine) showed significantly (P<0.05) serum total protein values than the group of birds fed diets supplementation of Methionine. However, non-significant (P<0.05) difference was supplemented synthetic Methionine or herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine). Similar results have been observed earlier by Kiran et al;(2012).
A significantly (P<0.05) higher blood glucose level was observed in the group of birds fed diets supplemented with herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine) when compared with the group of birds fed either synthetic methionine or without any supplemental Methionine. There was a significantly (P<0.05) linear decrease in serum cholesterol level with the supplementation of either synthetic or herbal Methionine with the most hypocholestrolemic effect observed with the supplementation of herbal Methionine (Nutri-Methionine).
CONCLUSION
The study concludes that 1kg Nutri-Methionine per tone of feed can efficiently replace 1kg synthetic DL-methionine per tone of feed to improve commercial Broiler performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are greatfully acknowledge and appreciate the financial support from M/s Nutricare Life Sciences Shaharnpur for conducting this research work.
Table. 1. Ingredient composition and chemical composition of basal diet.
Table. 2. Comparative effect of feeding diets supplemented with synthetic and herbal Methionine on the performance of broiler chicken.
REFERENCES
Anonymous 1999. Organic production of agricultural products and indications referring there to on agricultural products & food stuffs to include livestock products. Official J. European Committees. EU council regulation 1804/1999 pp 22.
Baker, D.H. 1991. Amino acid tolerance of Swine & poultry. In: NFIA Nutrition Institute handbook.
Bureau of Indain standard (BIS). 1992. Nutrient requirements for poultry. In: Animal feeds and Feeding stuffs. Determination of calcim and Magnesium in Mineral supplements IS, 13574.
Chattopadhayay, R.R. 2003. Possible mechanism of hepatoprotective activity of Azadirachta indica leaf extract:Part II. J. Ethnopharmacol; 89: 217-219.
Chattopadhayay,K., Mondal,M.K and Roy, B. 2006. comparative efficacy of DL-Methionine and herbal Methionine on performance of Broiler Chicken. International Journal of Poultry Science 5 (11):1034-1039.
Chen, F., Noll, S.L., Waibel, P.E and Hawkins. 1993. Effect of folate, vitamin B12 and choline supplementation on turkey breeder performance. Poult.Sci., 72:73.
Duncan, D.B. 1995. Multiple range and multiple”F” tests.Biometrics, 11:1-42.
Kadam, M.M., Gole, M.A and Kolte, B.R. 2009. comparative efficacy of DL-Methionine and semi-synthetic methionine (Nico meth) on broiler growth performance. Poultry Line (9) 49-51
Kalbande, V.H., Ravikanth, K., Maini, S and Rekhe, D.S. 2009. Methionine supplementation options in poultry. International Journal of Poultry Science 8 (6) & 588-591.
Kiran Kumari., Tiwari, S.P., Subhankar Nanda; Saxena, M.J., Ravikanth, K, and Maini Shivi. 2012. Studies on comparative efficacy of herbal aminoacid (Methiorep) supplement with synthetic DL-Methionine on Broiler growth performance and carcass quality traits. International Journal of Scientific and research Publication. 2 (8) 1-3.
Leeson, S and Summers, J.D. 2001. Nutrition of the chicken. 4th Edn; pp:112-125.
March, B and Biely, J. 1956. Folic acid supplementation of high protein-high fat diets. Poult.Sci., 35:550-551.
Narayananswami, H.D and Bahgwat,V.G. 2010. Evaluating the efficacy of Methionine supplementation options in commercial broiler chickens. Poultry Line. 3: 5-7.
Swick,R.A., Creswell, D.C., Dibner, J.J., Ivey, F.J. 1990. Impact of Methionine sorces on performance of broilers growing under warm and humid conditions. Poult.Sci., 69 (suppl.1):194 (Abstr.)
SPSS Base Applications Guide 7.5, ©, 1997. Statistical package for social sciences, Chicago,USA.