Mihaila Vasile
Forum: Fumonisine macroscopic leasons
To see the photo album, click here
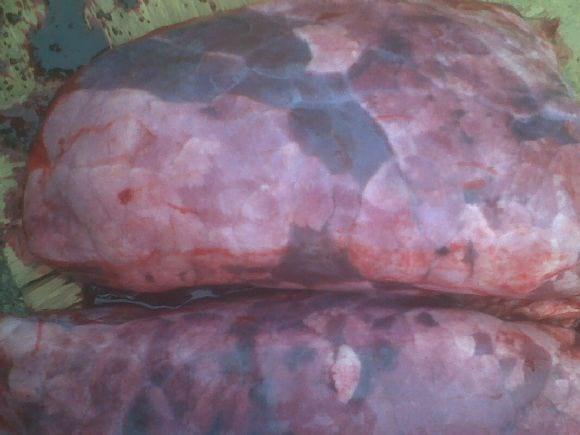
Where are the fumonisin lesions? This is typical mycoplasmosis + may be PRRS lesions...
This farm is free from PRRS, Aujeszky, APP all serotipes and is positive from M.hyo ( vaccination) and SIV ( H1N1, H2N3). M. hyo lessions are very specific and also Influenza has a very specifical clinical and anatomopathological signs. My first presumptive diagnostic was Pasteurella and we started to treat for this with Florfenicol bat without any significative improvement. We colected samples from blood, lungs, feed and water.
The only thing that we found was fumonisine levels to 10-24 times more than MLA. If somebody is interested I can show a lot of pictures not only with lungs because the anatomoclinical signs are diferentiated to the category of pigs. The most interesting signs that I found was hemorrhagic necrotic enteritis just in the duodenal area.
http://vdi.sagepub.com/content/5/2/232.full.pdf+html
Fumonisin Toxicosis in Swine: Clinical and Pathologic Findings
Billy M. Colvin,A. J. Cooley,and Rodney W. Beaver
J VET Diagn Invest, April 1993; vol. 5, 2: pp. 232-241.
From a series of experimental studies with pigs (12–16 kg), either pulmonary edema or liver failure emerged as a distinct pathogenetic expression of fumonisin B1 (FB1) toxicosis. The primary determinant as to which pathogenetic consequence developed was the quantity (dose) of the mycotoxin fed or intubated per kilogram of body weight per day. Pigs intubated with a minimum of 16 mg FB1/kg/day developed severe interlobular edema with or without hydrothorax and variably severe pulmonary edema. Pigs intubated with < 16 mg FB1/kg/day or pigs fed diets containing 200 mg FB1/kg of feed developed marked icterus and hepatocellular necrosis. The spectrum of degrees of severity of pulmonary edema observed in the experimental pigs allowed rational speculation regarding evolution of the pathologic changes.
I have the same problem, the lungs lesions are as in your photos. What mycotoxin binder do you use?
Hello,
I am not in pratice, I am a veterinary laboratory diagnostician
I supplied this reference because it pretty well illustrated the lung lesions caused by fumoninsin poisoning ie sever pulmonary oedema
Best regards
André Broes, D.V.M., Ph.D.
See also the following references:
http://toxicology.usu.edu/endnote/Characterization-fumonisin-toxicity.pdf
http://vdi.sagepub.com/content/5/3/413.full.pdf
Fumonisin Toxicosis in Swine: An Overview of Porcine Pulmonary Edema and Current Perspectives
On the picture It looks like PRRS lesions but I would check also for Actinobacillus Suis,
Thanks