Performance and intestinal health of broiler chickens supplemented with a protease and fed a standard diet or a low-density diet
The effect of a protease on performance and intestinal health of broiler chickens was evaluated when supplemented on top of a standard diet or in a low-density diet. Male Cobb chicks (392; 1-42d) were reared in floor pens and allocated in a completely randomized design in a 2x2 factorial arrangement with 7 replicates. There were 2 feed formulations: a standard diet (STD) and a low-density diet (LDD), with 6% reduction in crude protein and main digestible amino acids. The 2 diets were either supplemented (+P) or not (-P) with a protease (Jefo Protease at 125 g/t). The performance was evaluated by feeding period (1-7, 7- 21, 21-35 and 35-42d). At day 28, samples of ileum of two bird/replicate were analyzed by a morphometric index for histological alterations. There was no interaction between factors and no differences between the treatments were observed for the first 7 days of age. In general, for all the other periods, birds fed the LDD-P were lighter and/or had poorer feed conversion ratio (FCR) when compared to all other treatments (P < 0.05). The supplementation of the LDD with protease increased body weight gain (BWG) and decreased FCR (P < 0.05), promoting a performance similar to birds fed the STD-P. At 42d, the birds on the STD+P were the heaviest (124g difference to STD-P, P = 0.1) and presented the same FCR as the STD-P and LDD+P groups while being 13 points lower (P < 0.001) than the LDD-P group. Regarding the gut health analysis, birds receiving the protease presented the best morphological index (P ≤ 0.06) mainly as a result of fewer alterations of lamina propria and epithelial thickness and enterocyte proliferation. In conclusion, the protease improved performance and intestinal health indicators of broiler chickens when added on top of a standard diet or with a low-density diet.
I. INTRODUCTION
II. MATERIALS AND METHODS
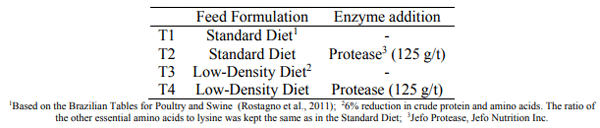
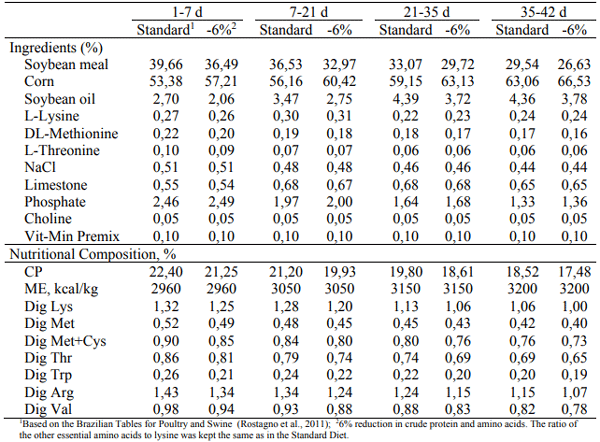
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
a) Intestinal health
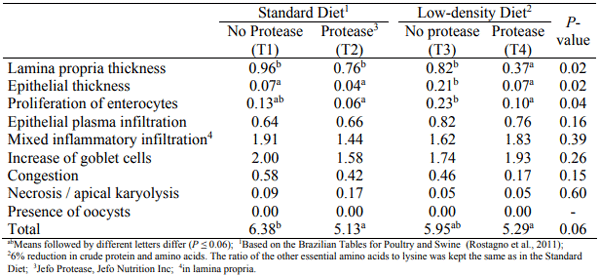
b. Performance
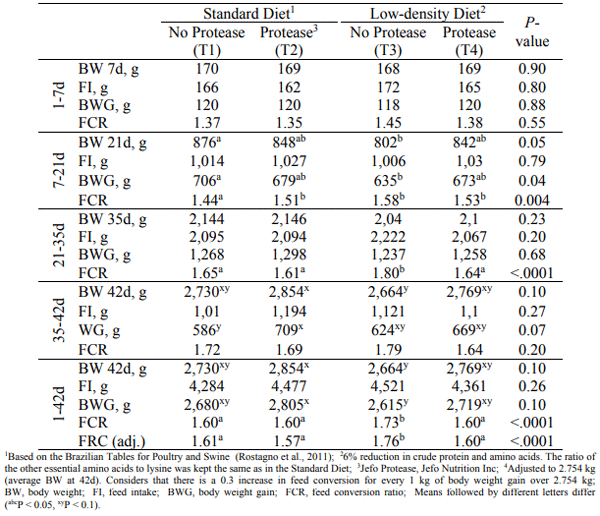
V. CONCLUSION
Kraieski AL, Hayashi RM, Sanches A, Almeida GC & Santin E (2017) Poultry Science 96: 1078-1087.
Lahaye L, Ávila González E, López Coello C, Arce Menocal J, Soto CE, Aguilera L, Detzler D & Bodin JC (2016) WPC2016 S1 0119: 48.
Rostagno HS, Albino LFT, Donzele JL, Gomes PC, Oliveira RF, Lopes DC, Ferreira AS, Barreto SLT & Euclides RF (2011) 3ªedição, Viçosa, MG: UFV, 252.
SAS Institute Inc. (2011) Base SAS® 9.3 Procedures Guide. SAS Institute Inc., Cary. NC, USA.
Wang CW, Qu MR, Gauthier R & Co R (2008) Acta Agriculturae Universitatis 30: 302-310.
Yu B, Wu ST, Liu CC, Gauthier R & Chiou PWS (2007) Animal Feed Science and Technology 134: 283-329.


























