Improving Utilisation of Soya Bean and Canola Meals with the Use of Multienzyme Solution in Broiler Chicken Diets
Published: December 22, 2021
By: R.A. PEREZ-MALDONADO 1, M. TOGHYANI 2, F. FRU-NJI 1, S. RAMIREZ 1 and A. COWIESON 1 / 1 DSM Japan K.K. Japan, 105-0011 Tokyo; 2 University of Sydney, Faculty of Science, Poultry Research Foundation, Camden NSW 2570, Australia.
Soybean meal (SBM) and canola meal (CM) are the main contributors to the protein fraction in poultry diets worldwide. However, these quality vegetable protein meals contain low molecular weight sugars (raffinose and stachyose) and cell wall pectic non-starch polysaccharides (NSPs), cellulose and hemicellulose (e.g. xyloglucans and mannans) which can be problematic. These NSPs are notorious for their water-holding capacity, increasing viscosity in the small intestine, impairing nutrient digestion and absorption and consequently inducing wet litter problems. When NSP-multienzyme combinations targeting specific fiber substrates are applied, the pectic and hemicellulose fiber components of SBM and CM walls are degraded, releasing valuable entrapped nutrients (Pedersen et al., 2015, 2017). The present study was conducted to ascertain if application of NSP-multienzyme blends, designed for specific fiber substrates, improve performance in broilers offered SBM and CM wheat-based diets. The positive control (PC) treatments were either SBM alone (PC1) or mixed with CM in the diets at 10, 18 and 27.5%, for starter, grower and finisher periods respectively, (PC2). In order to generate the negative control treatments for birds to underperform, these diets were imposed with an energy reduction of 70 Kcal (NC1 and NC2 for SBM and CM respectively). All dietary treatments received a background application of phytase (200 ppm Ronozyme Hi-Phos, Ca and avP matrix applied), xylanase (200 ppm Ronozyme WX, 60 Kcal matrix applied) and protease (200 ppm Ronozyme ProAct, 3-4% CP and AAs matrix applied). To test the effects of NSP-multienzyme combinations, the NC diets were supplemented with one of two commercial enzyme products (Ronozyme VP enzyme, VP, at 250 ppm alone; or VP combined with Ronozyme Multigrain enzyme, MG, at 100 ppm). There were seven replicate pens of 15 birds per treatment. Dietary treatments were fed for the starter (1-10 d), grower (11-24 d) and finisher (25-35 d) phases.
Table 1 - Effect of NSP-multienzyme on broiler chicken performance at 35 days of age.
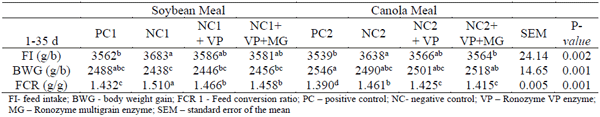
Table 1 illustrates that a 70 Kcal reduction imposed to the NC dietary treatments significantly affected (P< 0.05) bird performance, increasing FI and FCR compared to the PC diets. Birds fed the NC diets with NSP-multienzyme treatments presented a FI statistically similar to the PC treatment. For both protein sources, application of VP alone or with MG improved the FCR significantly compared to the NC diets (P< 0.05). Dietary treatments had no statistically significant impact on BWG within each protein meal. In conclusion, the NC diets increased FCR by approximately 8.0 and 7.0 points in NC-SBM and NC-CM diets, respectively. This deteriorated FCR was partly recovered by adding VP (4.4 and 3.6 points) and VP + MG (5.2 and 4.6 points) in SBM and CM diets, respectively.
Presented at the 30th Annual Australian Poultry Science Symposium 2020. For information on the next edition, click here.
References
Pedersen NR, Ravn JL, Pettersson D (2017) Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 234: 244-252.
Ravn JL, Martens, HJ, Pettersson D & Pedersen NR (2015) J. Agric. Sci. 7: 1-13.
Content from the event:
Related topics:
Authors:
dsm-firmenich
dsm-firmenich
Recommend
Comment
Share

Would you like to discuss another topic? Create a new post to engage with experts in the community.









.jpg&w=3840&q=75)