Gut Health, the pillar of entire health and production success
Published: October 26, 2022
By: Aminul Islam; DVM, MS.

“NO FOOT, NO HORSE '', an old saying among horsemen comes today as “NO GUT, NO POULTRY” among the poultry producers. Poultry producers know how important the gut is in efficient digestion of feed and nutrient utilization in the modern poultry production system. Intrinsic poultry studies well defined that the poultry gut is not just the sum of digestive organs but it combines highly proliferative epithelium, a diverse immune arms and a big set of ecological communities of microorganisms. The gut health indicates the state of all things associated with the entire digestive system and has a holistic role in the systemic health, welfare and production efficiency of birds. Therefore, gut health is very complex as it combines nutritional, microbiological, immunological and physiological aspects indeed to ensure a productive flock.
Gut components and Its Function
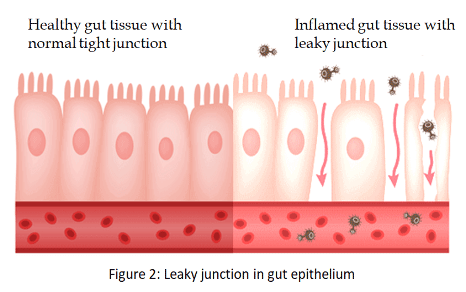
- Tissue: The gut is a tubular organ from mouth to end of cloaca and comprises with 5 distinct parts- the crop, proventriculus, gizzard, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum) and large intestine (ceca, colon and rectum). The inner surface of all these builds with an extraordinary single layer of cells called intestinal epithelium responsible for absorption of all the vital nutrients for the body, and along with mucus layer-composed of highly glycosylated proteins called mucins maintain an effective barrier against unwanted biological and non-biological particles. Unfortunately, this barrier sometimes fails to function as normal because of some associated factors and becomes permeable called ‘leaky gut’, which can lead to several health issues.
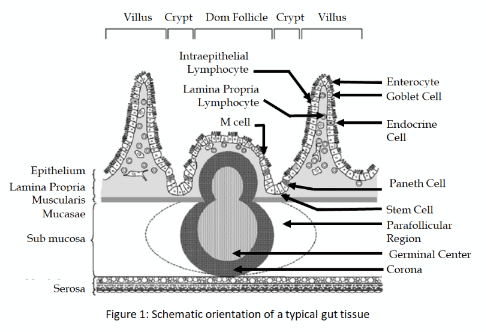
- Immunity: The gut is very important for immune function, with the wall providing a barrier that prevents pathogens from entering into the circulation and with the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), the largest mass of lymphoid tissue consisting of various immune cells- lymphocytes, macrophages, antigen-presenting cells etc.
- Microbiota: The introduction of next generation sequencing and other molecular techniques has greatly aided in the research on gut microbiota. Emerging evidence suggests that the gut microbiota is involved in regulating host health. The imbalance of gut microbiota leads to several gut issues commonly defined as dysbiosis.
Major factors of Gut Health Issues
A vast range of factors linked to diet, infectious agents, environment and farming practices can negatively affect the delicate balance among the components of the chicken gut and subsequently impair growth rate and feed conversion efficiency. Underdeveloped gut, delay in microbial establishment and weak gut health maintenance programme are some major predisposing factors for poor gut health. Poor nutrition, lower grade DOC, bad husbandry practice in the farm and compromising in the setting of gut health solutions can be the weak points in achieving good gut health.
Strategies to keep gut healthy
- Development: Without developing optimal gut tissues it is almost impossible to achieve a good gut for proper output. Along with good incubation progress, early a few days is very important for this development. Late initiative is almost useless, because research found that the most morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes occur during the first two weeks of post hatch and the most dramatic changes occur within the first 24 hours of hatching. For example, without proper development of GALT tissues, birds are left very prone to infectious disease susceptibility throughout their life.
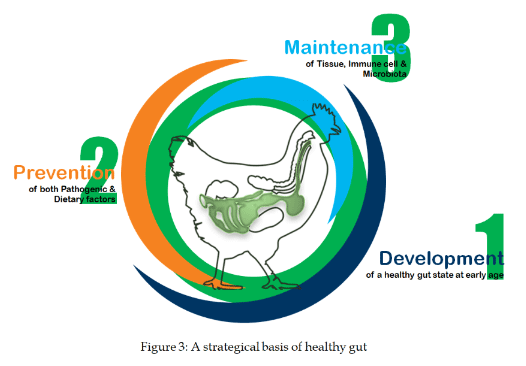
- Prevention: After developing a healthy tissue, the second most important target is to prevent these tissues from harmful effects of outsiders-both dietary factors and microbial invaders. Anti-nutritional factors in the diet and disease prevalent in the area are the matter to be prevented by prevention strategies.
- Maintenance: Success of all these initiatives fully depends on the maintenance approaches set to get optimum output from the gut. Stress; for example, flocks in high ambient temperature and free radicals that produce in the tissues have a remarkably bad impact on gut physiology and environment, thus all these can be prevented by suitable prevention strategies.
Surprisingly all stages of this strategy are very much interrelated and should be synchronized very carefully.
Therefore, when gut health is compromised, digestion and nutrient absorption are affected which, in turn, can have a detrimental effect on feed conversion leading to economic loss and a greater susceptibility to disease.
Disclaimer:The views expressed in this article are based on Author’s knowledge gathered from attending different seminars, webinars, symposiums, scientific journals and different articles published in internet media on gut health. The author will be pleased to deliver the sources of information upon due request.
Related topics:
Authors:
BioGreen International Limited
Recommend
Comment
Share
Recommend
Reply

Would you like to discuss another topic? Create a new post to engage with experts in the community.








.jpg&w=3840&q=75)