Transport and expression of transporters for 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and L-methionine along the intestine of broiler chickens receiving different methionine supplements
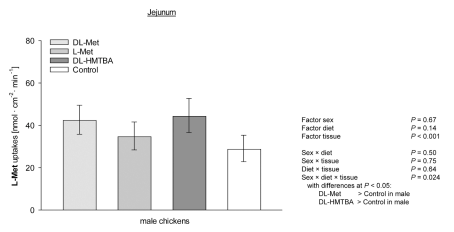
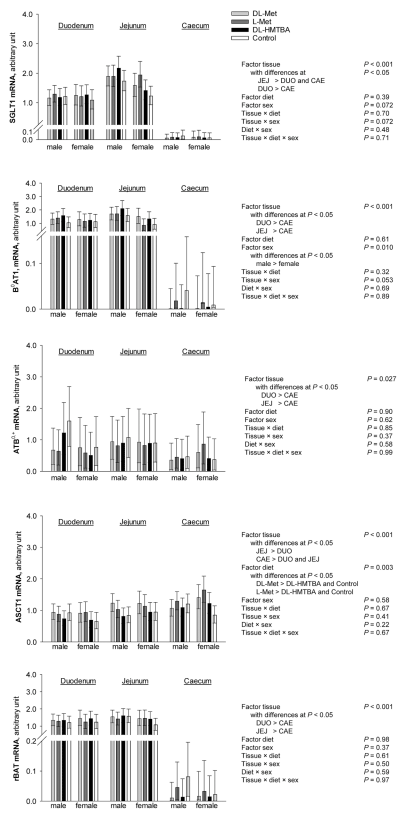
The present study hypothesized that supplementation of different methionine (Met) sources might influence the intestinal absorption of L-Met and 3-O-methyl-D-glucose (3-OMG) in broilers. In a completely randomized study, a total of 53 Cobb500 broilers (30 males and 23 females) received a grower-finisher diet that was either not supplemented with Met (Met + Cys, 0.49 %; control) or supplemented with either 0.27 % L-Met, 0.27 % DL-Met or 0.47 % DL-2‑hydroxy-4-(methylthio) butanoic acid (HMTBA). After ≥10 days on the diets, uptakes of 3-OMG and L-Met were measured in duodenum, mid-jejunum and caecum at 50 µM and 5 mM concentrations in Ussing chambers, each in the presence and absence of Na+. We also investigated the mRNA expression of apical glucose and Met transporters. Dietary supplements had no effect on 3-OMG and L-Met uptakes (P > 0.05), except for male broilers receiving DL-Met or DL-HMTBA, that showed higher jejunal uptakes of L-Met than control at 5 mM (P < 0.001). Except for L-Met uptakes at 5 mM, tissue × sodium interactions (P ≤ 0.05) for 3-OMG and L-Met uptakes verified higher uptakes in jejunum compared to duodenum and caecum; with higher uptakes in the presence vs. absence of Na+ in jejunum only. In duodenum, uptakes of L-Met and 3-OMG at 50 µM concentration were higher in males vs. females. Expression of SGLT1, B0 AT1, ATB0,+ and rBAT, but not ASCT1, were lowest in caecum (P ≤ 0.05). Expression of B0 AT1 was higher in males vs. females (P ≤ 0.05). Expression of ASCT1 was higher with DL-Met and DL-HMTBA supplements compared to L-Met and control (P ≤ 0.05). These findings indicate that jejunum is the main intestinal segment for Na+-dependent L-Met and 3-OMG absorption in broilers with minor effects of dietary Met source. A sexual dimorphism for duodenal nutrient uptake and mRNA abundance of B0 AT1 was congruent with the more efficient growth performance of male chickens known from the literature.
Introduction
Materials and methods
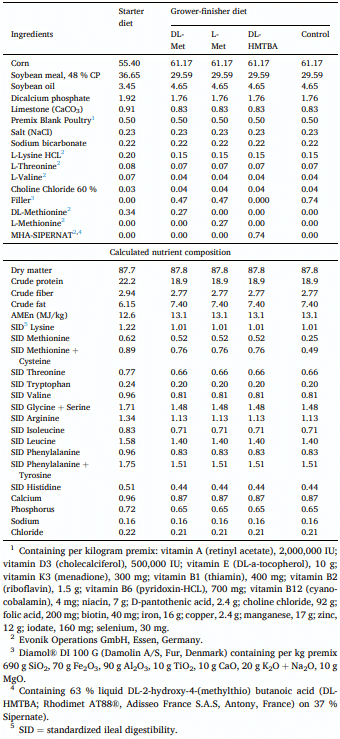
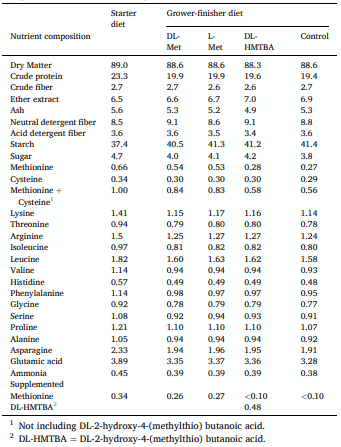
Animals and diets
Feed analysis
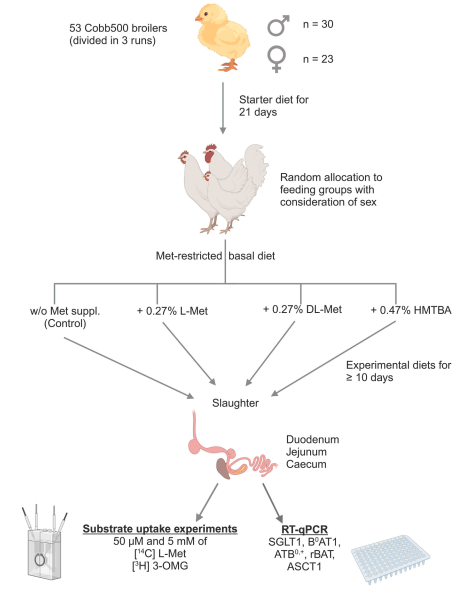
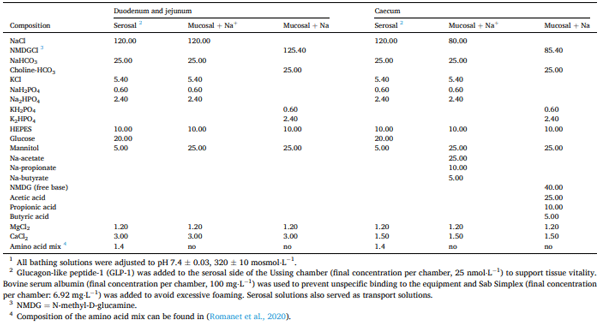
Tissue preparation and mounting
Ussing chamber experiments
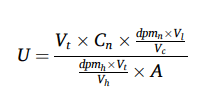
Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
Statistical analysis
Results
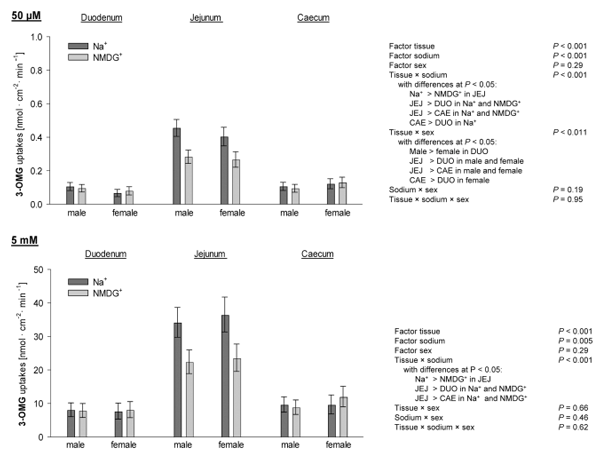
Apical uptakes of 3-OMG
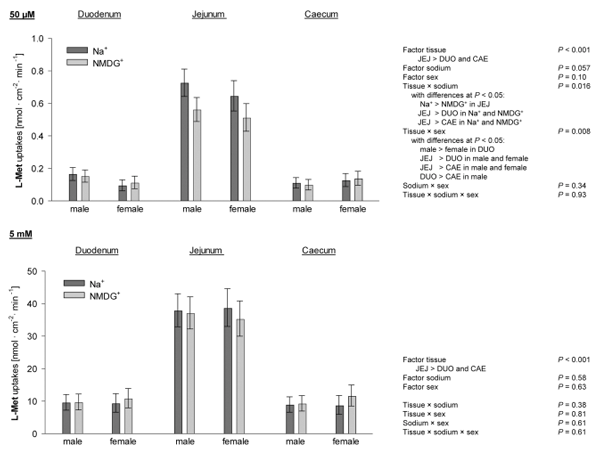
Apical uptakes of L-methionine
RT-qPCR
Discussion
Amat, C., Piqueras, J.A., Planas, J.M., Moreto, ´ M., 1999. Electrical properties of the intestinal mucosa of the chicken and the effects of luminal glucose. Poult. Sci. 8, 1126–1131.
Awad, W.A., Aschenbach, J.R., Setyabudi, F.M., Razzazi-Fazeli, E., Bohm, J., Zentek, J., 2007. In vitro effects of deoxynivalenol on small intestinal D-glucose uptake and absorption of deoxynivalenol across the isolated jejunal epithelium of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 1, 15–20.
Awad, W.A., Bohm, ¨ J., Razzazi-Fazeli, E., Hulan, H.W., Zentek, J., 2004. Effects of deoxynivalenol on general performance and electrophysiological properties of intestinal mucosa of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 12, 1964–1972.
Awad, W.A., Smorodchenko, A., Hess, C., Aschenbach, J.R., Moln´ ar, A., Dublecz, K., Khayal, B., Pohl, E.E., Hess, M., 2015. Increased intracellular calcium level and impaired nutrient absorption are important pathogenicity traits in the chicken intestinal epithelium during colonization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15, 6431–6441.
Azahan, E.A.E., Forbes, J.M., 1989. Growth, food-intake and energy-balance of layer and broiler-chickens offered glucose in the drinking-water and the effect of dietaryprotein content. Br. Poult. Sci. 4, 907–917.
Benyi, K., Tshilate, T.S., Netshipale, A.J., Mahlako, K.T., 2015. Effects of genotype and sex on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 7, 1225–1231.
Broer, A., Klingel, K., Kowalczuk, S., Rasko, J.E., Cavanaugh, J., Broer, S., 2004. Molecular cloning of mouse amino acid transport system B0, a neutral amino acid transporter related to Hartnup disorder. J. Biol. Chem. 23, 24467–24476.
Cobb&Vantress, 2022. Cobb 500 Broiler Performance & Nutrition Supplement, 10.
DLG Ausschuss Technik in der Tierhaltung, R.A., Uhlenkamp, A., Kammerling, ¨ D., Dohring, ¨ S., Berk, J., Grashorn, M., Werner, D., Mann, K.H., Bos, ¨ B., Mirbach, D., 2018. DLG-Merkblatt 438: Beleuchtung und Beleuchtungstechnik iM Geflügelstall. DLG E.V. Frankfurt, Germany.
Drew, M.D., Van Kessel, A.G., Maenz, D.D., 2003. Absorption of methionine and 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutoanic acid in conventional and germ-free chickens. Poult. Sci. 7, 1149–1153.
England, A., Gharib-Naseri, K., Kheravii, S.K., Wu, S.B., 2023. Influence of sex and rearing method on performance and flock uniformity in broilersdimplications for research settings. Anim. Nutrit. 12, 276–283.
Gesemann, M., Lesslauer, A., Maurer, C.M., Schonthaler, H.B., Neuhauss, S.C., 2010. Phylogenetic analysis of the vertebrate excitatory/neutral amino acid transporter (SLC1/EAAT) family reveals lineage specific subfamilies. BMC Evol. Biol. 10, 117.
Gilbert, E.R., Li, H., Emmerson, D.A., Webb Jr., K.E., Wong, E.A., 2007. Developmental regulation of nutrient transporter and enzyme mRNA abundance in the small intestine of broilers. Poult. Sci. 8, 1739–1753.
Giurgea, R., Coprean, D., Domide, A., Roman, I., 1991. Thiourea and methionine effects upon glucose and leucine absorption in chicken jejunum. Rev. Roum. Physiol. 1-2, 31–34.
ISO 12099:2017, 2017. Animal Feeding Stuffs, Cereals and Milled Cereal Products - Guideline for the Application of near Infrared Spectrometry, 2nd ed. ISO, Geneva, Switzerland.
Jando, J., Camargo, S.M.R., Herzog, B., Verrey, F., 2017. Expression and regulation of the neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 in rat small intestine. PLoS. One. 9, e0184845. Kaminski, N.A., Wong, E.A., 2018. Differential mRNA expression of nutrient transporters in male and female chickens. Poult. Sci. 1, 313–318.
Klünemann, M., Romero, L.F., Acman, M., Milfort, M.C., Fuller, A.L., Rekaya, R., Aggrey, S.E., Payling, L.M., Lemme, A., 2024. Multitissue transcriptomics demonstrates the systemic physiology of methionine deficiency in broiler chickens. Animal 5, 101143.
Laurino, P., Tawfik, D.S., 2017. Spontaneous emergence of S-adenosylmethionine and the evolution of methylation. Angew. Chem. Int .Ed. Engl. 1, 343–345.
Lemme, A., Hoehler, D., Brennan, J.J., Mannion, P.F., 2002. Relative effectiveness of methionine hydroxy analog compared to DL-methionine in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 6, 838–845.
Lemme, A., Li, Z.Y., Dorigam, J., 2024. Meta-analyses of methionine source concept validation trials in broilers. Animals 12, 1771.
Lemme, A., Naranjo, V., de Paula Dorigam, J.C., 2020. Utilization of methionine sources for growth and met+cys deposition in broilers. Animals 12, 2240. Lerner, J., Karcher, C.A., 1978. Kinetic-properties of an imino acid transport-system in chicken intestine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 4, 503–505.
Lerner, J., Sattelme, P., Rush, R., 1975. Kinetics of methionine influx into various regions of chicken intestine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Na1, 113–120.
Lindberg, J.E., 2023. Review: nutrient and energy supply in monogastric food producing animals with reduced environmental and climatic footprint and improved gut health. Animal Suppl 3, 100832. Llames, C.R., Fontaine, J., 1994. Determination of amino-acids in feeds - collaborative study. J. AOAC. Int. 6, 1362–1402.
Lopez, K.P., Schilling, M.W., Corzo, A., 2011. Broiler genetic strain and sex effects on meat characteristics. Poult. Sci. 5, 1105–1111.
Maenz, D.D., EngeleSchaan, C.M., 1996. Methionine and 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutanoic acid are partially converted to nonabsorbed compounds during passage through the small intestine and heat exposure does not affect small intestinal absorption of methionine sources in broiler chicks. J. Nutrit. 5, 1438–1444.
Mastrototaro, L., Sponder, G., Saremi, B., Aschenbach, J.R., 2016. Gastrointestinal methionine shuttle: priority handling of precious goods. IUBMB. Life. 12, 924–934.
McWhorter, T.J., Green, A.K., Karasov, W.H., 2010. Assessment of radiolabeled Dglucose and the nonmetabolizable analog 3-O-methyl-D-glucose as tools for In vivo absorption studies. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2, 376–384.
Miles, R.D., Butcher, G.D., Henry, P.R., Littell, R.C., 2006. Effect of antibiotic growth promoters on broiler performance, intestinal growth parameters, and quantitative morphology. Poult. Sci. 3, 476–485.
Miska, K.B., Fetterer, R.H., 2019. Expression of amino acid and sugar transporters, aminopeptidase, and the di- and tri-peptide transporter PepT1; differences between modern fast growing broilers and broilers not selected for rapid growth. Poult. Sci. 5, 2272–2280.
Mitchell, M.A., Lemme, A., 2008. Examination of the composition of the luminal fluid in the small intestine of broilers and absorption of amino acids under various ambient temperatures measured In vivo. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 7, 223–233.
Mitchell, M.A., Levin, R.J., 1981. Amino acid absorption in jejunum and ileum in vivo – a kinetic comparison of function on surface area and regional bases. Experentia 3, 265–266.
Moreto, M., Planas, J.M., 1989. Sugar and amino-acid-transport properties of the chicken Ceca. J. Exp. Zool. 3, 111–116.
Nickel, A., Kottra, G., Schmidt, G., Danier, J., Hofmann, T., Daniel, H., 2009. Characteristics of transport of selenoamino acids by epithelial amino acid transporters. Chem. Biol. Interact. 3, 234–241.
Palacin, M., 1994. A new family of proteins (rBAT and 4F2hc) involved in cationic and zwitterionic amino acid transport: a tale of two proteins in search of a transport function. J. Exp. Biol. 196, 123–137.
Riesenfeld, G., Sklan, D., Bar, A., Eisner, U., Hurwitz, S., 1980. Glucose-absorption and starch digestion in the intestine of the chicken. J. Nutrit. 1, 117–121.
Romanet, S., Aschenbach, J.R., Pieper, R., Zentek, J., Htoo, J.K., Whelan, R.A., Mastrototaro, L., 2020. Dietary supplementation of dl-methionine potently induces sodium-dependent L-methionine absorption in Porcine Jejunum ex vivo. J. Nutrit. 7, 1782–1789.
Romanet, S., Aschenbach, J.R., Pieper, R., Zentek, J., Htoo, J.K., Whelan, R.A., Mastrototaro, L., 2021. Expression of proposed methionine transporters along the gastrointestinal tract of pigs and their regulation by dietary methionine sources. Genes Nutr. 1, 14.
Romanet, S., Schermuly, I.I., Lemme, A., Zentek, J., Aschenbach, J.R., 2025. Optimizing the incubation solution for ex vivo investigations on intestinal tissues of chickens. Proc. Soc. Nutr. Physiol. 34, 51.
Ruan, T., Li, L., Lyu, Y., Luo, Q., Wu, B., 2018. Effect of methionine deficiency on oxidative stress and apoptosis in the small intestine of broilers. Acta. Vet. Hung. 1, 52–65.
Sklan, D., Geyra, A., Tako, E., Gal-Gerber, O., Uni, Z., 2003. Ontogeny of brush border carbohydrate digestion and uptake in the chick. Brit. J. Nutr. 6, 747–753.
Stein, E.D., Chang, S.D., Diamond, J.M., 1987. Comparison of different dietary aminoacids as inducers of intestinal amino-acid-transport. Am. J. Physiol. 5, G626–G635.
To, V., Masagounder, K., Loewen, M.E., 2021. Critical transporters of methionine and methionine hydroxyl analogue supplements across the intestine: what we know so far and what can be learned to advance animal nutrition. Comparat. Biochem. Physiol. a-Molecul. Integrat. Physiol. 255, 1109.
Torras-Llort, M., Torrents, D., Soriano-García, J.P., Gelpí, J.L., Est´evez, R., Ferrer, R., Palacín, M., Moreto, ´ M., 2001. Sequential amino acid exchange across b-like system in chicken brush border jejunum. J. Membr. Biol. 3, 213–220.
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., Speleman, F., 2002. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genom. Biol. 7.
Vazquez-Anon, M., Gonzalez-Esquerra, R., Saleh, E., Hampton, T., Ritcher, S., Firman, J., Knight, C.D., 2006. Evidence for 2-hydroxy-4(methylthio) butanoic acid and DLmethionine having different dose responses in growing broilers. Poult. Sci. 8, 1409–1420.
Vieira, S.L., Lemme, A., Goldenberg, D.B., Brugalli, I., 2004. Responses of growing broilers to diets with increased sulfur amino acids to lysine ratios at two dietary protein levels. Poult. Sci. 8, 1307–1313.
Vinardell, M.P., Lopera, M.T., Moreto, M., 1986. Absorption of 3-oxy-methyl-D-glucose by chicken cecum and jejunum in vivo. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. Comp. Physiol. 1, 171–173.
Wang, J.L., Dong, Y., Grewer, C., 2022. Functional and kinetic comparison of Alanine Cysteine serine transporters ASCT1 and ASCT2. Biomolecules 1, 113.
Wang, X., Peebles, E.D., Morgan, T.W., Harkess, R.L., Zhai, W., 2015. Protein source and nutrient density in the diets of male broilers from 8 to 21 d of age: effects on small intestine morphology. Poult. Sci. 1, 61–67.
Wang, Y.L., Yin, X.N., Yin, D.F., Lei, Z., Mahmood, T., Yuan, J.M., 2019. Antioxidant response and bioavailability of methionine hydroxy analog relative to DLmethionine in broiler chickens. Anim Nutrit. 3, 241–247.
Weintraut, M.L., Kim, S., Dalloul, R.A., Wong, E.A., 2016. Expression of small intestinal nutrient transporters in embryonic and posthatch turkeys. Poult. Sci. 1, 90–98.
Wu, G., Fang, Y.Z., Yang, S., Lupton, J.R., Turner, N.D., 2004. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 3, 489–492.
Yodseranee, R., Bunchasak, C., 2012. Effects of dietary methionine source on productive performance, blood chemical, and hematological profiles in broiler chickens under tropical conditions. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 8, 1957–1963.
Zhang, S., Saremi, B., Gilbert, E.R., Wong, E.A., 2017. Physiological and biochemical aspects of methionine isomers and a methionine analogue in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2, 425–439.
Zhang, Y., Zhuang, Z., Mahmood, T., Mercier, Y., Jin, Y., Huang, X., Li, K., Wang, S., Xia, W., Wang, S., Yu, M., Chen, W., Zheng, C., 2023. Dietary supplementation with 2-hydroxy-4-methyl(thio) butanoic acid and DL-methionine improves productive performance, egg quality and redox status of commercial laying ducks. Anim. Nutrit. 3, 101–110.



















