Introduction
The presence of mycotoxins in feed grains is rious for both broilers and broiler performance. In order to reduce the negative effects of mycotoxins in animals, mycotoxin-adsorbing additives with different neutralization abilities are used.
The purpose of this study was to determine the in vitro aflatoxin-adsorbing ability of T5X SD in broilers.
Materials and Methods
The study was undertaken in Samitec institute, RS, Brazil.
The Aflatoxin B1 Standard, Sigma Chemical Co., in an acetonitrile solution was used as the test mycotoxin. Adsorption assays were performed in triplicate using artificial gastric fluid (pH 3.0) and artificial intestinal fluid (pH 6.0), as per the National Formulary Pharmacopeia - USP XXII (1990).
T5X SD concentrations tested were 12 - 50 mg/10 mL. In other words, the maximum adsorbent-toxin ratio was 5000:1. The analysis was performed using an automated system with ASPEC XL4 pre-column derivatization, under mass spectrometry-coupled liquid chromatography (LC/MS/MS).
Result interpretation/analysis was performed using the ChemStation Agilent SystemTM.
Results and Discussion
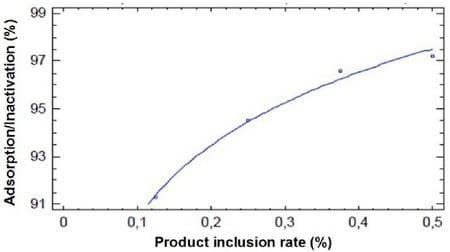
The adsorption regression in the gastric fluid (pH 3.0) is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Adsorption/inactivation regression of aflatoxin B1 at pH 3.0
Adsorption = 100.573 + 4.41113* (adsorbent dose rate)
Adsorption/inactivation linear equation = 89.95 + 15.85 * (Adsorbent dose rate)
R² = 0.9950 P = 0.00
The % adsorption of T5X SD (inclusion rate, 0.50%) in the gastric fluid (pH 3.0) for aflatoxin B1 (1.0 µg/ml) was 97.22% (± 0.76).
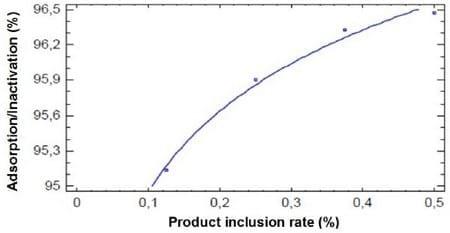
The adsorption regression in the intestinal fluid (pH 6.0) is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Adsorption/inactivation regression of aflatoxin B1 at pH 6.0
Adsorption = 97.2304 + 0.988656 * (adsorbent dose rate)
Adsorption/inactivation linear equation = 94.85 + 3.53 * (Adsorbent dose rate)
R² = 0.9938 P = 0.00
The % adsorption of T5X SD (inclusion rate: 0.50%) in the intestinal fluid (pH 6.0)for aflatoxin B1 (1.0 µg/ml) was 96.47% (± 1.64).
Conclusions
The anti-mycotoxin T5X SD feed additive showed a high aflatoxin adsorption/inactivation coefficient at both pH 3.0 (97.22%) and pH 6.0 (96.47%).
Acknowledgements
Gratitude is expressed to the Samitec Institute (Santa Maria, RS, Brazil) for the funds to carry out this study.
This paper was originally presented in Portuguese at the XXII Latin American Poultry Congress in Buenos Aires, Argentina, August, 2011. It´s been translated with the purpose of sharing the results with English speakers.









.jpg&w=3840&q=75)