Crude Oil Prices and its effects on Feed Additives
Impact of crude oil price trends on feed additives’ prices
Published: May 26, 2011
By: Dr Shirish Nigam & Meenakshi Tiwari (Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd.)
Introduction
As the world´s population continues to increase, demands for food will experience dramatic growth. This coupled with raising affluence in developing nations, will shape the eating habits of the global population. Protein rich foods particularly meat consumption raises when disposable incomes rises. Consequently, the animal food industry and its allied sectors are set to experience major growth. Analysts have observed that this demand is influenced my many factors, commodity prices being single largest determinant. Prices of commodities again are governed by many economic factors. The focus of our current communication will be to assess the effect of crude-oil price on commodities and their influence on feed additives.
Animal Feed additives comprise just one percent of the volume of feed but can cost as much as ten percent of the total cost. This segment therefore is always closely evaluated by feed manufacturers and farmers. The broad commercial term "Animal feed additive" generally comprises the two major technical segments - supplements and additives which include amino acids, vitamins, minerals and antibiotic and non antibiotic performance Promoters. Table 1 shows the different feed additives that use a petrochemical derivative as a raw material in its industrial manufacturing process. Fluctuation in crude oil prices logically will impact the prices and availability of these additives.
Table 1: Showing various feed additive which have petrochemicals raw material
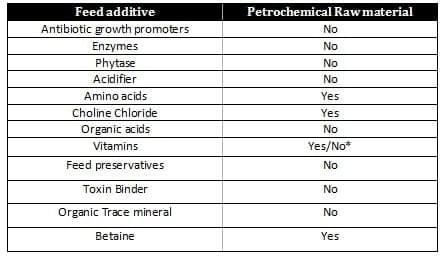
*Some vitamins are derived from petrochemical raw materials
Crude oil prices outlook and analysis
Crude-oil prices have been a real indicator of world economy. Tracking past economic activity and crude-oil prices, it can be said both variables have cause-effect relation. Assuming that global growth will be 3 percent per annum from year 2000 to 2030; the International Energy Agency has projected that global oil demand will increase by 1.66 % annually over the same period, leading to a two -third rise in global demand for oil, to 120 million barrels per day. This in turn will cause consistent increase in oil price approximately $8/ barrels per year. The crude oil price trends for last 5 years are summarized in table 2 and chart 1 below.
Table 2: Showing crude-oil prices in last five years
Chart 1: Showing crude-oil prices in last three years
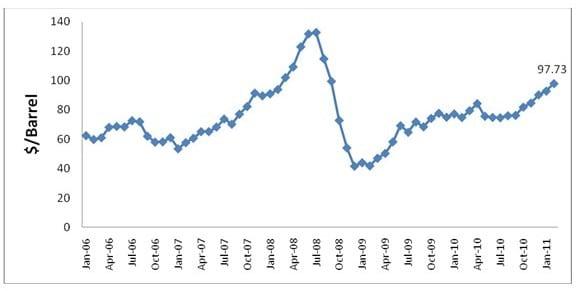
Major fluctuations on crude oil prices can be seen in year 2008, 2009 and 2010. The reason for fluctuation could be:
- 2008:
- One of the most widely believe reason for rise in price of crude oil in 2008 was overheating of world economy and hence increase in demand for crude oil and petroleum related product.
- Loss of Nigerian output due to presence of sulphur content in their oil, which went against policy of US and many European companies.
- The oil price increase prior to mid-2008 was also attributed partly to weaker dollar
- 2009:
- 2009 saw decline crude oil prices in first half and gradual increase in second half, this can be attributed to following reason:
- Declines in many other commodities prices as a global recession ( in economic activity) occurred.
- Demand for any commodity is price-elastic, which means that once the price goes too high, consumers stop buying it or make heroic efforts to find a substitute.
- 2010:
- 2010 saw increase in crude-oil due to signs of recovery in the global economies, hence increase in demand.
- Weakening of American dollar was another reason for rise crude oil prices.
- Revival in US economy by the end of 2010, which is one of highest consumer of crude and petroleum related product.
- China can be cited as other reason, where demand for crude oil rose by 20%.
- 2011:
- 2011 initial three month saw crude oil price hovering around $90/barrel and expected to rise in coming rest month (Brent crude and WTI, crude oil index were hovering around $120/barrel on 23rd April). Primary reason for rise in crude-oil price in 2011 from January till March was disturbances in Middle East countries, primary producer of crude oil. While other reasons are:
- World demand growth: The expected increase in world demand for Oil in 2011: IEA (International Energy Agency) expects petroleum demand worldwide in 2011 to be 88.8 million barrels per day, which is roughly a 1.6% increase in demand for oil in 2011 compares to 2010; in 2010 the daily consumption was estimated at 87.4 MB/d.
- Middle East crisis: Middle East crisis is another major reason for spike in oil prices, main reason for it being rising uncertainty over supply side. Other than that recent earthquake in Japan and further failure of its Nuclear plant will put further pressure on demand for crude-oil prices.
- China´s demand in 2011: On the one hand, Asia´s demand for energy is responsible for 70% of the world energy growth in the past couple of decades, in which China was responsible for 40% of it. Also, China´s energy demand nearly tripled since 1990. On the other hand, as presented above, it´s expected that China´s growth in demand for crude oil will decrease compare to 2010. This slowdown could be because of China´s fight to cool down its economy as there inflation pressures increase (as of Nov 2010, the Y-2-Y inflation rate was 5.1%). Therefore, China´s role in driving crude oil price higher will remain to be seen.
- U.S. dollar: The U.S. has taken several steps in the past couple of years that reduced the value of the dollar against major commodity markets and drove them high (such as gold prices). As the U.S. dollar continue to lose its appeal and worth, investors will keep on relying on the commodity market and consequentially will drive commodities prices up, including crude oil price.
- Europe´s recovery: the Euro zone is also a key player in consuming crude oil, and as the year will progress, Europe´s recovery from the recent slowdown could affect crude oil demand and price.
Impact of crude oil cost on DL-Methionine
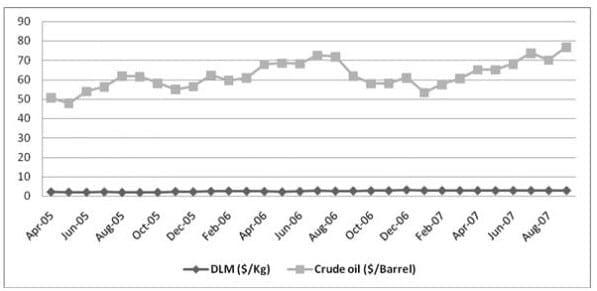
Methionine is an essential amino acid, which play critical role in broiler production as the first limiting amino acids. DL-methionine is manufactured exclusively from petrochemical raw materials (Propene and Methanol) by a chemical process. Table 2 and chart 2 show the data on the prices of Dl-methionine and Crude oil through the last 5 financial years. A direct correlation between the two price trends ( 0.41) is seen.
Table 3: showing crude and DLM prices
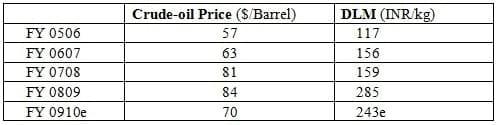
Graph 3: showing average DLM and crude-price trend for past year 2005-07
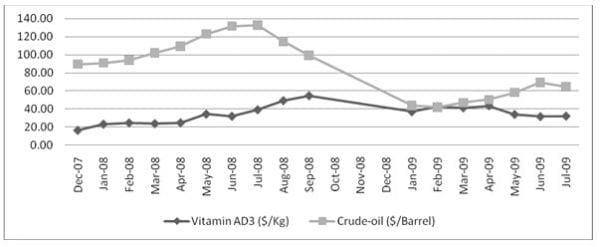
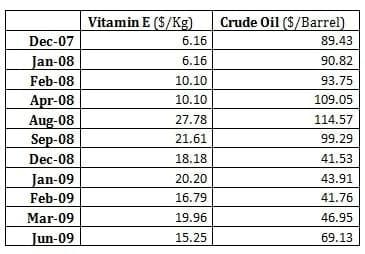
Impact of crude oil cost on Vitamin AD3 & E prices
Raw materials for these two are Acetone, Acetylene, Tri-methyl phenol, Isobutylene, Formaldehyde, Ethylene, Isoprene, and Iso-valeraldehyde. So, Vitamin A and E has petrochemical raw material. Hence we can also conclude that Vitamin AD3 has petrochemical raw material. Inspite of both vitamins raw material of crude-origin, correlation between Vitamin AD3 and E prices with Crude-oil stand to be negative i.e. -0.1477 and -0.1730 respectively in 2007-09 period. Here other economic factor has important role to play in determining prices of Vitamins, which need further investigation.
1. Vitamin AD3
Table 4: Showing Crude price & AD3 price
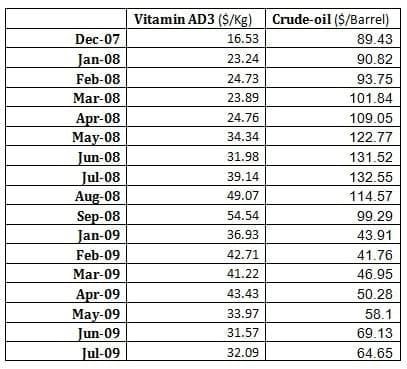
Graph 4: Graph showing price trend for Vitamin AD3 and Crude-oil
Vitamin E
Table 5: Table showing price trend for Vitamin-E and crude-oil
Graph 5: Graph showing price trend for Vitamin-E and crude-oil in 2010
Impact of crude oil cost on Choline Chloride
Raw materials for Choline chloride are Trimethylamine (TMA), Ethylene Oxide (EO) and Hydrochloric Acid (HCl). Here both TMA and EO are petrochemical raw material.
Table 6: Showing correlation between different variable
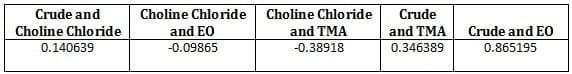
*Choline Chloride prices are taken of Jubilant´s Choline Chloride
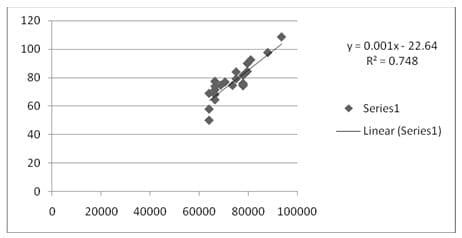
Now from above table, we can clearly conclude that there is significant correlation in crude and ethylene oxide prices. However that hasn´t been passed on to our choline prices, which definitely going to hit our bottom-line.
Table 7: Showing pricing for Choline Chloride and its raw material and crude oil for past two year
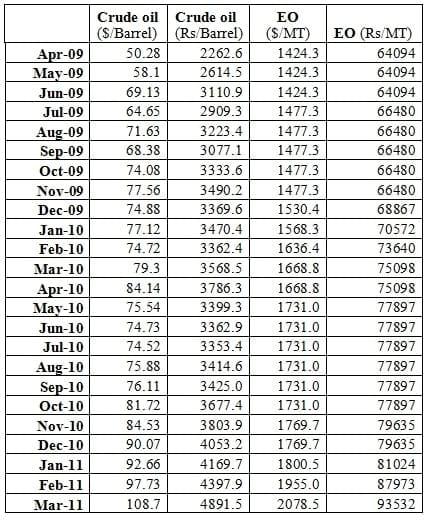
Graph 6: Depicts relation between crude-oil and Ethylene Oxide
Impact of crude oil cost on Lysine
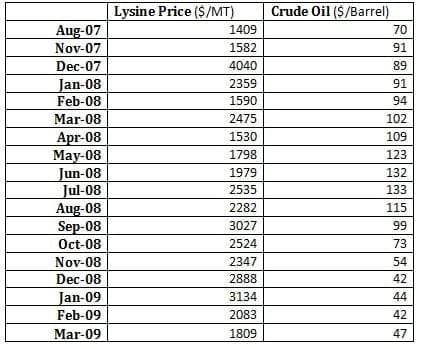
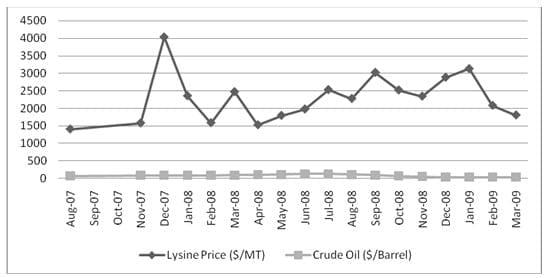
Lysine is industrially produced by microbial fermentation, from a base mainly of sugar. One the major raw material for Lysine is methanol. Lysine is an important additive to animal feed because it is a limiting amino acid when optimizing the growth of certain animals such as pigs and chickens for the production of meat. However correlation between Lysine and crude-oil comes out to be negative i.e. -0.15. This means that the period which we have taken i.e. 2007-09 might have other economic factor which are playing major role for movement of Lysine price in opposite direction with the respect to crude prices.
Table 8: Table showing price trend for Lysine and crude-oil
Graph 7: Graph showing price trend for Lysine and crude-oil in 2010
Impact of crude oil cost on Betaine
Betaine is another feed additive where crude-oil price fluctuation affect has been studied. Raw materials required for manufacturer of synthetic Betaine are trimethylamine (TMA) & mono-chloro acetic acid and both are of crude-origin. However relation between TMA and Betaine prices was not significant and also crude oil and Betaine prices weren´t significant. This can be due to Betaine being new-age feed additive, where impacts of crude-oil prices haven´t been felt yet. It leaves us with further investigation on Betaine price in reference to crude prices in coming future.
Conclusion
- DL-Methionine price is quite significantly related to crude price (correlation being 0.41). DLM had multiple effect of increase in crude prices due to one of the raw material for the same being methanol, whose demand increases with increase in crude prices and second reason being same of petro-origin.
- Vitamin AD3 and Vitamin E correlation with crude prices was -0.1477 and -0.1730.
- Ethylene oxide price has significant correlation with crude-price. However effect of it is still not visible on Choline Chloride (as price change of raw material is not being completely passed on final product). However this trend cannot be carried for long, and if this trend continues in near future Choline Chloride prices are bound to be effected.
- Again Lysine price has negative correlation with crude prices, which need further investigation in respect to other economic variable.
- Betaine price wasn´t seemed to be significantly correlated with crude prices inspite its raw material being of crude-origin. It must be because Betaine is relatively new concept in feed industry and we require more time for further investigation on relation between crude and Betaine prices.
Related topics:
Authors:
EW Nutrition
Recommend
Comment
Share

16 de febrero de 2012
According to a recent survey, gasoline costs in the U.S. have increased by almost 12 cents a gallon over the past three weeks. The price increase is held accountable, at least in part, on the rising price of crude oil in the North Sea. Those Middle Eastern tensions include threats by Iran to block vital shipping lanes, the higher cost of summer-grade fuel and a decreased refinery capacity. Another factor affecting the hike is increased gasoline consumption in developing nations, such as India and China. Consumer spending is necessary for the economy to improve and recover.
Recommend
Reply
Vamso Biotec Pvt Ltd.
14 de junio de 2011
Hi Dr. Nigam,
Really nice way of interpretations. You have put the things in a very lucid manner. Good job!!
Dr. Arindam Chatterjee
Recommend
Reply

Would you like to discuss another topic? Create a new post to engage with experts in the community.







.jpg&w=3840&q=75)