Postbiotics: An Alternative for Improving Health and Performance of Poultry Production
Author details:
The gastrointestinal tract has the largest surface area of the body and if it is subjected to continuous stress, it will activate the immune system. The intestinal barrier, the immune system, and the microbiota together form a line of defense against infection in order to maintain a healthy balance between the host and the microbiota. Nutritional strategies such as feed additives can be applied to maintain homeostasis in the gastrointestinal tract. When this equilibrium is disrupted, metabolic dysfunctions can occur. Postbiotics—the metabolic and/or structural compounds of microorganisms—can stimulate anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and enzymatic effects, providing a safe alternative to establishing intestinal eubiosis. In addition, postbiotics can be used as an alternative to antibiotics in broiler diets by maintaining productive performance under challenging conditions. This review provides an overview of the postbiotic concept, mechanism of action and production, the evidence for the action in the gastrointestinal tract, and applications in poultry production.
Keywords: antioxidant; broiler; eubiosis; intestinal health; intestinal inflammation; postbiotics
1. Introduction
2. Postbiotics: Understanding the Concept and the Mechanisms of Action
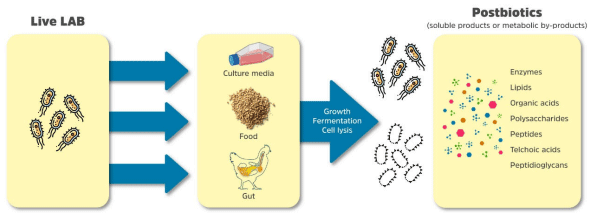
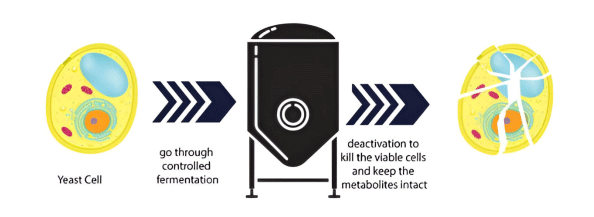
3. Postbiotics: Methods of Production and the Main Compounds
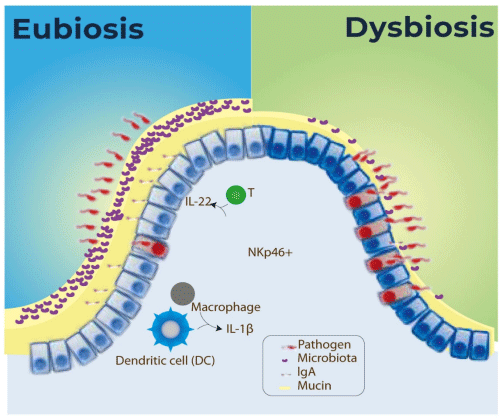
4. Eubiosis and Gut Health: Microbiota and Gut Barrier
5. Reported Impacts on Productivity and Poultry Health
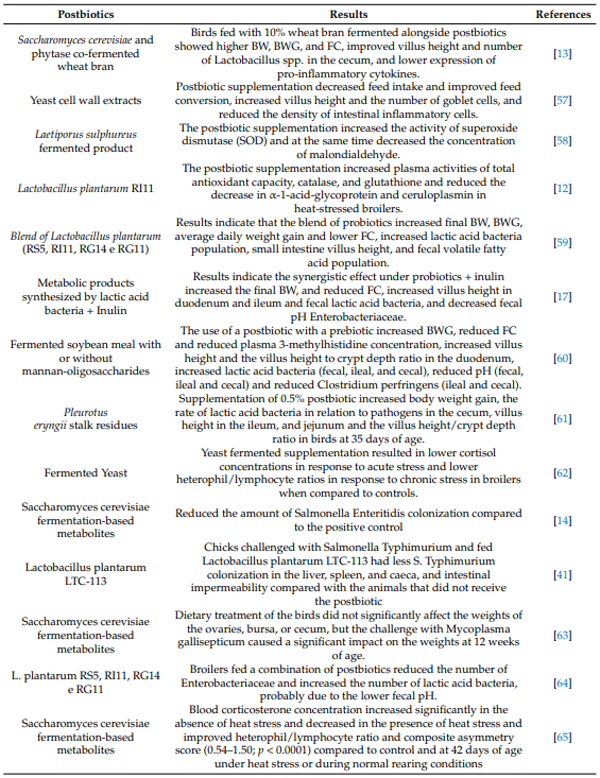
5.1. Antioxidant Action and Meat Quality Interactions
5.2. Intestinal Morphology and Performance Enhance
5.3. Immune System Modulation and Pathogen Control
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
1. Skelly, A.N.; Sato, Y.; Kearney, S.; Honda, K. Mining the Microbiota for Microbial and Metabolite-Based Immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 305–323. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
2. Wegh, C.A.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Knol, J.; Roeselers, G.; Belzer, C. Postbiotics and Their Potential Applications in Early Life Nutrition and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4673. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
3. Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You Are What You Eat: Diet, Health and the Gut Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 35–56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
4. Leeming, E.R.; Johnson, A.J.; Spector, T.D.; Le Roy, C.I. Effect of Diet on the Gut Microbiota: Rethinking Intervention Duration. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2862. [CrossRef]
5. Wan, M.L.Y.; Ling, K.H.; El-Nezami, H.; Wang, M.F. Influence of Functional Food Components on Gut Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 1927–1936. [CrossRef]
6. Sun, X.; Zhai, J. Research Status and Trends of Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Diseases Based on Bibliometrics. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 673. [CrossRef]
7. Mosca, F.; Giannì, M.L.; Rescigno, M. Can Postbiotics Represent a New Strategy for NEC? Probiotics Child Gastrointest. Health: Adv. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Public Health 2019, 10, 37–45. [CrossRef]
8. Zółkiewicz, J.; Marzec, A.; Ruszczy ´nski, M.; Feleszko, W. Postbiotics—A Step beyond Pre- and Probiotics. ˙ Nutrients 2020, 12, 2189. [CrossRef]
9. Chambers, L.; Avery, A.; Dalrymple, J.; Farrell, L.; Gibson, G.; Harrington, J.; Rijkers, G.; Rowland, I.; Spiro, A.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; et al. Translating Probiotic Science into Practice. Nutr. Bull. 2019, 44, 165–173. [CrossRef]
10. Rad, A.H.; Abbasi, A.; Kafil, H.S.; Ganbarov, K. Potential Pharmaceutical and Food Applications of Postbiotics: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 1576–1587. [CrossRef]
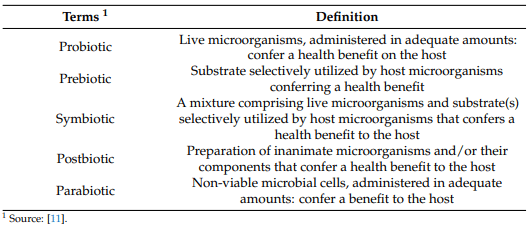
11. Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) Consensus Statement on the Definition and Scope of Postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
12. Humam, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Izuddin, W.I.; Awad, E.A.; Idrus, Z.; Samsudin, A.A.; Mustapha, N.M. Dietary Supplementation of Postbiotics Mitigates Adverse Impacts of Heat Stress on Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, Total Antioxidant, Lipid Peroxidation, Physiological Stress Indicators, Lipid Profile and Meat Quality in Broilers. Animals 2020, 10, 982. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
13. Chuang, W.-Y.; Lin, L.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-C.; Lee, T.-T. Effects of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Phytase Co-Fermentation of Wheat Bran on Growth, Antioxidation, Immunity and Intestinal Morphology in Broilers. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1157–1168. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
14. Gingerich, E.; Frana, T.; Logue, C.M.; Smith, D.P.; Pavlidis, H.O.; Chaney, W.E. Effect of Feeding a Postbiotic Derived from Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Fermentation as a Preharvest Food Safety Hurdle for Reducing Salmonella Enteritidis in the Ceca of Layer Pullets. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 275–280. [CrossRef]
15. Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.J. The Health Effects of Cultured Milk Products with Viable and Non-Viable Bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 749–758. [CrossRef]
16. Siciliano, R.A.; Reale, A.; Mazzeo, M.F.; Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M. Paraprobiotics: A New Perspective for Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1225. [CrossRef]
17. Kareem, K.Y.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Akit, H.; Samsudin, A.A. Effects of Dietary Postbiotic and Inulin on Growth Performance, IGF1 and GHR MRNA Expression, Faecal Microbiota and Volatile Fatty Acids in Broilers. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 163. [CrossRef]
18. Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Wei, F.; Wen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Y. Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals the Roles of Cecal Microbiota and Its Derived Bacterial Consortium in Promoting Chicken Growth. mSystems 2023, 8, e0084423. [CrossRef]
19. Vinderola, G.; Sanders, M.E.; Salminen, S. The Concept of Postbiotics. Foods 2022, 11, 1077. [CrossRef]
20. Jastrz ˛ab, R.; Graczyk, D.; Siedlecki, P. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Influenced by Postbiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13475. [CrossRef]
21. Moradi, M.; Molaei, R.; Guimarães, J.T. A Review on Preparation and Chemical Analysis of Postbiotics from Lactic Acid Bacteria. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 143, 109722. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
22. Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.S.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; HernándezMendoza, A. Postbiotics: An Evolving Term within the Functional Foods Field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [CrossRef]
23. María José, H.-G.; Elena, F.-R. Postbiotics in Human Health: Possible New Functional Ingredients? Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109660. [CrossRef]
24. Zawistowska-Rojek, A.; Tyski, S. How to Improve Health with Biological Agents—Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1700. [CrossRef]
25. Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-Parabiotics: The New Horizons in Microbial Biotherapy and Functional Foods. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 168. [CrossRef]
26. Pelyuntha, W.; Chaiyasut, C.; Kantachote, D.; Sirilun, S. Cell-Free Supernatants from Cultures of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Grape as Biocontrol against Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Typhimurium Virulence via Autoinducer-2 and Biofilm Interference. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7555. [CrossRef]
27. Fong, W.; Li, Q.; Yu, J. Gut Microbiota Modulation: A Novel Strategy for Prevention and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4925–4943. [CrossRef]
28. Khodaii, Z.; Ghaderian, S.M.H.; Natanzi, M.M. Probiotic Bacteria and Their Supernatants Protect Enterocyte Cell Lines from Enteroinvasive Escherichia Coli (EIEC) Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2017, 6, 183–189. [CrossRef]
29. Homayouni Rad, A.; Aghebati Maleki, L.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Abbasi, A. Postbiotics: A Novel Strategy in Food Allergy Treatment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 492–499. [CrossRef]
30. Mantziari, A.; Salminen, S.; Szajewska, H.; Malagón-Rojas, J.N. Postbiotics against Pathogens Commonly Involved in Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1510. [CrossRef]
31. Ruas-Madiedo, P. Detection, Isolation, and Purification of Bifidobacterial Exopolysaccharides. Bifidobact. Methods Protoc. 2021, 2278, 101–115. [CrossRef]
32. Zhong, Y.; Wang, S.; Di, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Gut Health Benefit and Application of Postbiotics in Animal Production. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 38. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
33. De Marco, S.; Sichetti, M.; Muradyan, D.; Piccioni, M.; Traina, G.; Pagiotti, R.; Pietrella, D. Probiotic Cell-Free Supernatants Exhibited Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity on Human Gut Epithelial Cells and Macrophages Stimulated with LPS. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1756308. [CrossRef]
34. León, E.D.; Francino, M.P. Roles of Secretory Immunoglobulin A in Host-Microbiota Interactions in the Gut Ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 880484. [CrossRef]
35. Martyniak, A.; Medy ´nska-Prz˛eczek, A.; W˛edrychowicz, A.; Skocze ´n, S.; Tomasik, P.J. Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, Paraprobiotics and Postbiotic Compounds in IBD. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1903. [CrossRef]
36. Pfefferle, P.I.; Prescott, S.L.; Kopp, M. Microbial Influence on Tolerance and Opportunities for Intervention with Prebiotics/Probiotics and Bacterial Lysates. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1453–1463. [CrossRef]
37. Fisher, J.F.; Mobashery, S. Constructing and Deconstructing the Bacterial Cell Wall. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 629–646. [CrossRef]
38. Hernández, S.B.; Dörr, T.; Waldor, M.K.; Cava, F. Modulation of Peptidoglycan Synthesis by Recycled Cell Wall Tetrapeptides. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107578. [CrossRef]
39. Bortoluzzi, C.; Pedroso, A.A.; Mallo, J.J.; Puyalto, M.; Kim, W.K.; Applegate, T.J. Sodium Butyrate Improved Performance While Modulating the Cecal Microbiota and Regulating the Expression of Intestinal Immune-Related Genes of Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3981–3993. [CrossRef]
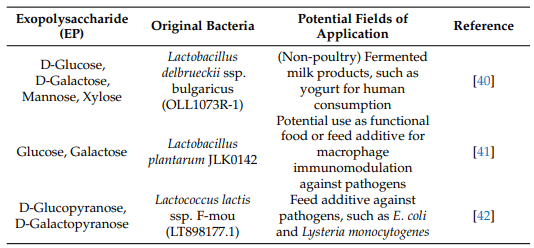
40. Makino, S.; Ikegami, S.; Kano, H.; Sashihara, T.; Sugano, H.; Horiuchi, H.; Saito, T.; Oda, M. Immunomodulatory Effects of Polysaccharides Produced by Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Ssp. Bulgaricus OLL1073R-1. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2873–2881. [CrossRef]
41. Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Fang, X.; Min, W.; Yang, Z. Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of an Exopolysaccharide Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum JLK0142 Isolated from Fermented Dairy Tofu. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 985–993. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
42. Nehal, F.; Sahnoun, M.; Smaoui, S.; Jaouadi, B.; Bejar, S.; Mohammed, S. Characterization, High Production and Antimicrobial Activity of Exopolysaccharides from Lactococcus Lactis F-Mou. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 10–19. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
43. Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [CrossRef]
44. Kayama, H.; Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Interaction Between the Microbiota, Epithelia, and Immune Cells in the Intestine. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 23–48. [CrossRef]
45. Rychlik, I. Composition and Function of Chicken Gut Microbiota. Animals 2020, 10, 103. [CrossRef]
46. Aruwa, C.E.; Pillay, C.; Nyaga, M.M.; Sabiu, S. Poultry gut health—Microbiome functions, environmental impacts, microbiome engineering and advancements in characterization technologies. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 119. [CrossRef]
47. Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Impacts of Gut Bacteria on Human Health and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493–7519. [CrossRef]
48. Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. 1), S17–S30. [CrossRef]
49. Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Mardani, K.; Ezati, P. Efficacy of lyophilized cell-free supernatant of Lactobacillus salivarius (Ls-BU2) on Escherichia coli and shelf life of ground beef. Vet. Res. Forum 2019, 10, 193–198. [CrossRef]
50. Li, H.-Y.; Zhou, D.-D.; Gan, R.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Shang, A.; Xu, X.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3211. [CrossRef]
51. Alam, A.; Neish, A. Role of Gut Microbiota in Intestinal Wound Healing and Barrier Function. Tissue Barriers 2018, 6, 1539595. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
52. Gutiérrez, S.; Fischer, J.; Ganesan, R.; Hos, N.J.; Cildir, G.; Wolke, M.; Pessia, A.; Frommolt, P.; Desiderio, V.; Velagapudi, V.; et al. Salmonella Typhimurium Impairs Glycolysis-Mediated Acidification of Phagosomes to Evade Macrophage Defense. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009943. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
53. Hortová-Kohoutková, M.; Lázniˇcková, P.; Friˇc, J. How Immune-Cell Fate and Function Are Determined by Metabolic Pathway Choice. BioEssays 2021, 43, 2000067. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
54. Macpherson, A.J.; Slack, E. The functional interactions of commensal bacteria with intestinal secretory IgA. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 23, 673–678
55. Azad, M.A.K.; Sarker, M.; Wan, D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics on Cytokine Profiles. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8063647. [CrossRef]
56. Karimi, S.; Rashidian, E.; Birjandi, M.; Mahmoodnia, L. Antagonistic Effect of Isolated Probiotic Bacteria from Natural Sources against Intestinal Escherichia Coli Pathotypes. Electron. Physician 2018, 10, 6534–6539. [CrossRef]
57. Pascual, A.; Pauletto, M.; Giantin, M.; Radaelli, G.; Ballarin, C.; Birolo, M.; Zomeño, C.; Dacasto, M.; MBortoletti; Vascellari, M.; et al. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Yeast Cell Wall Extracts on Performance and Gut Response in Broiler Chickens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. /J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 40. [CrossRef]
58. Lin, W.C.; Lee, T.T. The Laetiporus Sulphureus Fermented Product Enhances the Antioxidant Status, Intestinal Tight Junction, and Morphology of Broiler Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 149. [CrossRef]
59. Thanh, N.T.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Hair-bejo, M.; Azhar, B.K. Effects of Feeding Metabolite Combinations Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum on Growth Performance, Faecal Microbial Population, Small Intestine Villus Height and Faecal Volatile Fatty Acids in Broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 298–306. [CrossRef]
60. Soumeh, E.A.; Mohebodini, H.; Toghyani, M.; Shabani, A.; Ashayerizadeh, A.; Jazi, V. Synergistic Effects of Fermented Soybean Meal and Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Growth Performance, Digestive Functions, and Hepatic Gene Expression in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6797–6807. [CrossRef]
61. Lai, L.P.; Lee, M.T.; Chen, C.S.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.T. Effects of Co-Fermented Pleurotus Eryngii Stalk Residues and Soybean Hulls by Aureobasidium Pullulans on Performance and Intestinal Morphology in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2959–2969. [CrossRef]
62. Nelson, J.R.; Sobotik, E.B.; Athrey, G.; Archer, G.S. Effects of Supplementing Yeast Fermentate in the Feed or Drinking Water on Stress Susceptibility, Plasma Chemistry, Cytokine Levels, Antioxidant Status, and Stress- and Immune-Related Gene Expression of Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3312–3318. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
63. Elliott, K.E.C.; Branton, S.L.; Evans, J.D.; Leigh, S.A.; Kim, E.J.; Olanrewaju, H.A.; Pharr, G.T.; Pavlidis, H.O.; Gerard, P.D.; Peebles, E.D. Growth and Humoral Immune Effects of Dietary Original XPC in Layer Pullets Challenged with Mycoplasma Gallisepticumabc. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3030–3037. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
64. Loh, T.C.; Thanh, N.T.; Foo, H.L.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Azhar, B.K. Feeding of Different Levels of Metabolite Combinations Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum on Growth Performance, Fecal Microflora, Volatile Fatty Acids and Villi Height in Broilers. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 205–214. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
65. Price, P.T.; Byrd, J.A.; Alvarado, C.Z.; Pavlidis, H.O.; McIntyre, D.R.; Archer, G.S. Utilizing Original XPCTM in Feed to Reduce Stress Susceptibility of Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 855–859. [CrossRef]
66. Aristides, L.G.A.; Venancio, E.J.; Alfieri, A.A.; Otonel, R.A.A.; Frank, W.J.; Oba, A. Carcass Characteristics and Meat Quality of Broilers Fed with Different Levels of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Fermentation Product. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3337–3342. [CrossRef]
67. Choe, D.W.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Awis, Q.S. Egg Production, Faecal PH and Microbial Population, Small Intestine Morphology, and Plasma and Yolk Cholesterol in Laying Hens given Liquid Metabolites Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum Strains. Br. Poult. Sci. 2012, 53, 106–115. [CrossRef]
68. West, C.; Stanisz, A.M.; Wong, A.; Kunze, W.A. Effects of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae or Boulardii Yeasts on Acute Stress Induced Intestinal Dysmotility. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10532. [CrossRef]
69. Takadanohara, H.; Catanzaro, R.; Chui, D.H.; He, F.; Yadav, H.; Ganguli, A.; Sakata, Y.; Solimene, U.; Minelli, E.; Kobayashi, R.; et al. Beneficial Effect of a Symbiotic Preparation with S. Boulardii Lysate in Mild Stress-Induced Gut Hyper-Permeability. Acta Biomed 2012, 83, 208–216.
70. Gou, H.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Ren, L.-F.; Li, Z.-J.; Zhang, L. How Do Intestinal Probiotics Restore the Intestinal Barrier? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929346. [CrossRef]
71. Van Coillie, E.; Goris, J.; Cleenwerck, I.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Botteldoorn, N.; Van Immerseel, F.; De Buck, J.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; Herman, L.; et al. Identification of Lactobacilli Isolated from the Cloaca and Vagina of Laying Hens and Characterization for Potential Use as Probiotics to Control Salmonella Enteritidis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 102, 1095–1106. [CrossRef]
72. Canonici, A.; Siret, C.; Pellegrino, E.; Pontier-Bres, R.; Pouyet, L.; Montero, M.P.; Colin, C.; Czerucka, D.; Rigot, V.; André, F. Saccharomyces Boulardii Improves Intestinal Cell Restitution through Activation of the α2β1 Integrin Collagen Receptor. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18427. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
73. Abdulkarimi, R.; Daneshyar, M.; Aghazadeh, A. Thyme (Thymus Vulgaris) Extract Consumption Darkens Liver, Lowers Blood Cholesterol, Proportional Liver and Abdominal Fat Weights in Broiler Chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 10, e20. [CrossRef]
74. Humam, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Samsudin, A.A.; Mustapha, N.M.; Zulkifli, I.; Izuddin, W.I. Effects of Feeding Different Postbiotics Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum on Growth Performance, Carcass Yield, Intestinal Morphology, Gut Microbiota Composition, Immune Status, and Growth Gene Expression in Broilers under Heat Stress. Animals 2019, 9, 644. [CrossRef]
75. Kaufman, J.D.; Seidler, Y.; Bailey, H.R.; Whitacre, L.K.; Bargo, F.; Lüersen, K.; Rimbach, G.; Pighetti, G.M.; Ipharraguerre, I.R.; Ríus, A.G. A Postbiotic from Aspergillus Oryzae Attenuates the Impact of Heat Stress in Ectothermic and Endothermic Organisms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6407. [CrossRef]
76. Najafi, P.; Zulkifli, I.; Soleimani, A.F.; Goh, Y.M. Acute Phase Proteins Response to Feed Deprivation in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 760–763. [CrossRef]
77. Jansseune, S.C.; Lammers, A.; van Baal, J.; Blanc, F.; van der Laan, M.H.P.; Calenge, F.; Hendriks, W.H. Diet composition influences probiotic and postbiotic effects on broiler growth and physiology. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103650. [CrossRef]
78. Jansseune, S.C.; Blanc, F.; Lammers, A.; van Baal, J.; Bruneau, N.; Pinard-van der Laan, M.H.; Hendriks, W.H.; Calenge, F. Microbiota but not immune modulation by a pro- and postbiotic was associated with the diet-additive interaction in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104184. [CrossRef]
79. Forder, R.E.; Willson, N.-L.; Angove, J.A.; McWhorter, T.J.; McQueen, M.A.; Cadogan, D.J. Dietary inclusion of a saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite improved reproductive performance but did not affect intestinal permeability in two chicken meat breeder lines. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103595. [CrossRef]
80. Ramlucken, U.; Lalloo, R.; Roets, Y.; Moonsamy, G.; van Rensburg, C.J.; Thantsha, M.S. Advantages of bacillus-based probiotics in poultry production. Livest. Sci. 2020, 241, 104215. [CrossRef]
81. Ramlucken, U.; Ramchuran, S.O.; Moonsamy, G.; Lalloo, R.; Thantsha, M.S.; Jansen van Rensburg, C. A novel bacillus based multi-strain probiotic improves growth performance and intestinal properties of clostridium perfringens challenged broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 331–341. [CrossRef]
82. Ghareeb, K.; Awad, W.A.; Mohnl, M.; Porta, R.; Biarnés, M.; Böhm, J.; Schatzmayr, G. Evaluating the efficacy of an avian-specific probiotic to reduce the colonization of Campylobacter jejuni in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1825–1832. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
























