Dietary Betaine Supplementation as a Functional Nutrient in the Least-Cost Feed Formulation
Published: February 2, 2023
By: Md. Rabiul Awal, B.Sc A.H, MBA.
Introduction:
Betaine has been known as a functional nutrient widely used in animal nutrition during the last decade. It’s the trimethyl derivative of glycine, and is present in many plants and animal tissues such as aquatic invertebrates and sugar beets.
As a feed additive, betaine is commonly used as anhydrous, monohydrate, and betaine hydrochloride. According to the latest research, the nutritional properties of betaine HCL is equal to anhydrous while offering less cost and more non-hygroscopicity.
Due to the chemical structure, betaine has many functions at the gastrointestinal and metabolic levels in poultry and ruminants. Dietary supplementation of betaine plays important role in osmoregulation, methyl group donation, nutrient digestibility, and feed cost reduction by replacing two important nutrients- choline and methionine.
Betaine as a methyl group donor:
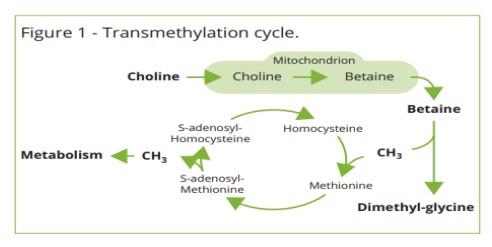
Dietary supplementation of betaine may be used directly as a methyl group donor whereas its precursor choline needs to be converted to betaine which requires a two-step enzymatic reaction in the mitochondria of liver and kidney cells. Methionine availability is a key factor both in protein synthesis and the formation of SAM that can be replaced by alternative methyl group donor which performs regeneration of methionine. Thus, the addition of betaine in the feed may result in the reduction of other methyl group donor requirements such as methionine and choline.
As a methyl group donor betaine increases the production of methylated metabolites during the transmethylation reaction, such as carnitine which is important for energy retention during growth and peak production period. Carnitine is responsible for the transport of fatty acids in the mitochondria of liver cells where fatty acid oxidation takes place, resulting decrease in fatty liver disease.
Betaine, as a methyl donor, is important for the synthesis of protein, DNA/RNA, nucleic acids, detoxification of AFB1, and immunomodulation.
Betaine as Osmoregulator:
The effect of heat stress causes production impairments in broiler and laying hens such as reduction in feed intake, increase of energy expenditures, metabolic disorder, cell death, etc.
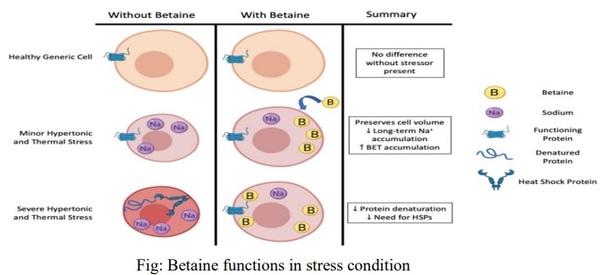
Betaine is a dipolar zwitterion and highly soluble in water thus functioning as an osmoregulator. It increases the water retention capacity of the intestinal and muscle tissues by holding water against the concentration gradient. Maintaining the balance of water and ions within the cell is very important for the survivability of cells in stress conditions as well as the good health and peak performance of birds.
It reduces the necessity for the ionic pump function of the intestinal cells which results in reduced energy expenditure and boosts performance by ensuring more energy is available.
Some study shows that betaine can reduce faecal water content by 30-35%, which results in lowering dirty eggs number and improving overall benefits of laying hen.
Betaine is considered as the most effective osmoprotectant among the other organic osmolytes due to its function of reaching high intracellular concentrations without causing disturbance to important cellular metabolism and DNA replication. By replacing inorganic ions, betaine protects the functioning enzymes and proteins from denaturation and deactivation thus allowing the cell to maintain its metabolic activities to continue proliferation.
Betaine as gut health enhancer:
As an osmoregulator, betaine reduces the high osmotic concentrations of salt and solutes in the gastrointestinal tract which improves microbial fermentation. In this condition volatile fatty acids and lactic acid production increases. These acids may lower the pH in the intestine, and stimulates pancreatic secretion, therefore increasing nutrient digestibility. Betaine has positive effect on intestinal cell proliferation, and increases villus height to provide a wider surface for better nutrient absorption which results in a higher return on investment.
Some research shows that betaine may inhibit coccidial invasion and development by improving intestinal structure and function, and maintaining water balance. Betaine might improve the efficacy of coccidiostats by resulting in a synergistic effect.
Betaine in Nutrient digestibility and Carcass modification:
Betaine enhances the digestibility of minerals, crude fiber, neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber in the intestine. It also enhances lipase activity and decreases the level of cholesterol in the serum of laying hens.
Betaine is known as carcass modifier due to its involvement in lipid metabolism. Methyl group enhances the synthesis of lecithin which improves fat digestion and absorption. Betaine is the precursor of glycine which in association with bile acids forms bile salts. Bile salts enhance fat digestion and absorption in the body, therefore, increasing carcass weight.
Betaine in feed cost reduction:
Betaine can partially replace methionine and choline chloride in feed to reduce production costs. Choline has a bioefficacy of 55% to betaine. Betaine is more efficient in increasing liver betaine levels compared to an equimolar amount of choline, but betaine can be used as a replacement part only for the methyl group donor function of choline.
Considering and calculating the chemical equivalence, molecular weight, and bioavailability correction it could be claimed that 2.1 units of choline chloride are equal to 1 unit of betaine, on a 100% purity basis. Studies on laying hens show that supplementation of betaine to diets with no added choline could maintain stable performance during peak production.
On the other hand, as compared to methionine, 1.4 units of methionine are equal to 1 unit of betaine, on a 100% purity basis. Some studies revealed that betaine could be as effective as methionine in promoting growth and feed efficiency in broilers.
As the raw materials price hike is trending upward worldwide, therefore, replacing choline and methionine fully or partially with betaine can reduce feed costs remarkably.
However, the potential of dietary betaine as a substitute for methionine and choline in the diet is variable and subject to undertaking consideration of the available raw materials nutrition, and ration specifications.
Conclusion:
Betaine supports normal physiological functions as well as production performance during high ambient temperature and under stress conditions by acting as an osmoregulator and functioning cellular metabolism. In the gastrointestinal tract, betaine might provide nutrition to the epithelial cells and therefore resulting in gut tissue integrity, increased villus length to provide more surface for nutrient absorption. Betaine promotes intestinal microbes for microbial fermentation activity which may result in nutrient digestibility.
Betaine supports liver function, reducing fatty livers and increasing both growth and laying performance. Betaine, as a methyl donor involved in methylation reaction and supports protein and DNA synthesis. It can partially replace methionine and choline to be used in the least cost ration formulation.
Disclaimer: The pieces of information expressed in this article are based on the Author’s knowledge and findings from different scholarly articles, technical journals, seminars and webinars, research and trials facilitated by betaine manufacturers. Author will be pleased to provide references on request.
Related topics:
Authors:
Ace pharmaceutical
Recommend
Comment
Share

Would you like to discuss another topic? Create a new post to engage with experts in the community.






