Importance of Bile Acids in Shrimp Nutrition and Hepatopancreas
Published: January 1, 2002
By: Nancy Yang, Marketing & Sales Director, Lachance
The health of hepatopancreas is one of the keys to successful shrimp farming, but the damage of hepatopancreas of shrimp often occurs during the farming process. This article mainly discusses the importance of shrimp hepatopancreas and the effects of bile acids on the hepatopancreas health.
The hepatopancreas, also known as the midgut gland, are located in the head and chest, the front end of the midgut, and the two sides of the stomach in the shrimp body, which are composed of two symmetrical petals. As the largest functional organ of shrimp, the hepatopancreas not only synthesizes and secretes digestive enzymes, stores fat and glycogen, but also absorbs and digests nutrients, and affects animal excretion and molting cycle. Many outbreaks of diseases like EMS, WFS are also closely related to the health of the hepatopancreas. Once the hepatopancreas are damaged on a large scale, other organs and growth of the shrimp will collapse. The hepatopancreas are composed of four major functional cells:
E cells: Embryonic cells that can divide into other hepatopancreatic cells.
F cells: Digestive enzyme cells that secrete digestive enzymes into the hepatopancreas duct and midgut.
R cells: Cells for absorbing and storing energy mainly in the form of lipids, and also for storing glycogen and mineral elements, which accounts for 60%-70% of hepatopancreatic cells.
B cells: Cells for intracellular digestion.
F cells: Digestive enzyme cells that secrete digestive enzymes into the hepatopancreas duct and midgut.
R cells: Cells for absorbing and storing energy mainly in the form of lipids, and also for storing glycogen and mineral elements, which accounts for 60%-70% of hepatopancreatic cells.
B cells: Cells for intracellular digestion.
The integrity of these four cellular structures is the basis for the normal functions of the hepatopancreas.
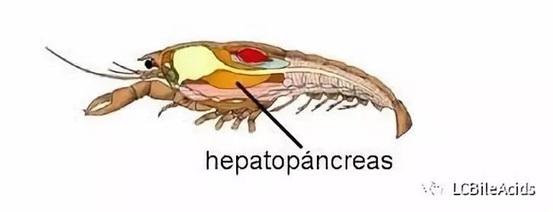
Bile acids are the major constituents of bile formed by the combination of the cholesterol or taurine and produced in the liver. The main functions of bile acids are promote fat digestion and protect liver health. As a functional additive to promote the digestion and absorption of lipids by the hepatopancreas and discharge toxins, bile acids play the following roles in shrimp farming:
Bile acids promote the digestion and absorption of fat, cholesterol and other nutrients, improves growth, and increase final weight.
- To emulsify triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol: HLB value of bile acids is 19 so bile acids have a strong emulsification function, which can emulsify large fat particles into oil-in-water type small particles for better fat digestion.
- To activate lipase activity and complete fat hydrolysis: The lipase secreted by the F cell is in the form of a zymogen with a weak ability to digest fat, however, when combined with bile acids, it can expose its catalytic groups for better digestion.
- To improve the storage capacity of lipids to provide energy for molting: During molting, the shrimps stop feeding, and all energy supplies depend on the fat stored in the hepatopancreas. In addition, in the process of molting, the body needs to absorb energy from the mineral elements in the water. Therefore, the storage of lipids plays a significant role in the shrimp molting, which directly affects the survival rate in the molting process.
Bile acids protect hepatopancreas health, increase the survival rate.
The basis of hepatopancreas health is the integrity of the four functional cell struc- tures. Bile acids play the protection role from the following four aspects:
- Against the free radical damage. Bile acids can increase the activity of SOD, GSH- Px and PO in hepatopancreas. Remove reactive oxygen species, reduce MDA content, resist environmental stress and enhance detoxification ability. Maintain the sta- bility of hepatopancreas cell structure and hepatopancreas health.
- Improve fat utilization and protect R cell structure. Bile acids increase lipase activity and promote digestion and absorption of triacylglycerols, phospholipids and cholesterol. Fat utilization efficiency plays an important role in maintaining the normal physiological structure of R cells. The presence of certain lipid droplets in R cells has become one of the physiological indicators of the healthy level of hepatopancreas.
Experiment Group:15 days after adding bile acids, the hepatopancreas of the vannamei were densely packed with fat and hepatopancreas were healthy.
Control Group:15 days after the same feed without bile acids, the hepatopancreas fat particles are sparse and in a sub-healthy state.
- Detoxification. Bile acids combines with mycotoxins, algae toxins and bacterial endotoxins in the hepatopancreas, and excretes them from the intestine. On the other hand, it promotes R cells to enrich heavy metal ions in water and remove heavy metal toxins. So as to achieve detoxification and detoxification, protect the hepatopancreas.
- Inhibit harmful bacteria. Bile acids inhibit the proliferation of harmful bacteria and reduce the release of bacterial endotoxin.
Bile acids prevent soft shell and other abnormality molting phase
In shrimp farming, shrimps are often found to be molting failure and soft-shell phenomenon.
Molting failure: mainly occurs in the late stage of molting, which is characterized by the death of shrimp during molting. Except for a few cases caused by bacterial infections, mainly because the hepatopancreas of the shrimp are not healthy enough.
There is not enough energy to store: less fat storage. From the early stage of the molting the shrimp stop feeding, and the energy consumption is basically dependent on the fat stored in the hepatopancreas. If the fat storage in the hepatopancreas are not enough, after the energy is exhausted it will cause the death of shrimps.
Soft-shell phenomenon: mainly occurs after the molting, the calcification of the shrimp shell is slow. and the outer skin is thin and soft. This kind of shrimp is easily stabbed by other shrimps and cause bacterial infection. Soft-shell is mainly caused by two reasons:
1. Mineral elements in water are less and ion concentration is low.
2. Ion absorption in water is a energy-consuming process. The insufficient storage of fat in hepatopancreas and the slow absorption of ions in water result in soft shell. Therefore, the basic reason for the failure of molting and soft-shell is that the hepatopancreas of shrimp are not healthy and the fat storage not enough. The addition of bile acid can effectively promote the enrichment of fat in hepatopancreas, maintain the health of hepatopancreas and reduce the various problems during molting. In addition, bile acids can also improve the utilization of essential nutrients such as cholesterol and reduce the using of cholesterol to achieve a balance between breeding benefits and feed costs.
Control of WFS by using bile acids
WFS is not just a bowel disease, the occurrence of WFS is often accompanied by lesions of the liver and pancreas. The section observation revealed that the white stool contained: liver lesion tissue, mucus, intestinal mucosa and undigested complete pep- tone. WFS treatment, not only to maintain intestinal health, but more importantly to protect the liver and pancreas.
In addition to protecting the hepatopancreas and repairing hepatopancreas, bile acids acts as an effective fungicide. Bile acids inhibits the excessive proliferation of intestinal bacteria and maintains the intestinal micro-ecological environment: due to the sur- face activity of bile acids, deoxycholic acid. It can destroy the cell membrane of bacteria, impair cell integrity, thereby inhibiting the growth of bacteria and even causing bacterial cell death. Thereby effectively preventing and treating the occurrence of WFS.
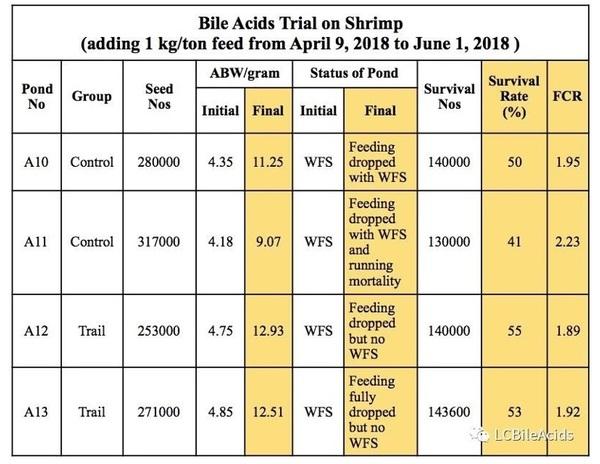
After using bile acids in feed, WFS problem in experiment groups was totally solved; the average survival rate of the experiment groups increased by 18.7% compared with the control group; the final average body weight and average weight gain of the experiment groups were respectively 25.2% and 34.4% higher than those of control groups.
Conclusion: as a new type of feed additive, bile acids can be widely used in shrimp feed, with the functions to sustain hepatopancreas health and improve the growth performance.
Related topics:
Authors:
Lachance
Recommend
Comment
Share
Recommend
Reply

2 de enero de 2021
Can I use bile acid in eggcustard for larvae of fresh water prawn?
Recommend
Reply

Would you like to discuss another topic? Create a new post to engage with experts in the community.




.jpg&w=3840&q=75)